From my experience, I’ve seen how foundries produce such clean and strong aluminum castings. If you work in this field, you understand that even tiny particles of debris can ruin an entire production run. I believe this is where ceramic filters prove their worth. They effectively remove contaminants and also create a smoother, more even flow. Most discussions I hear center on removing impurities, but I think these filters offer more than that. So, what do I see as the most significant advantage?
Purposes and Benefits of Ceramic Filters for Aluminum Casting
Ceramic filters help your operations and save you money. I find their main jobs are simple: they take out unwanted bits and manage how the liquid aluminum flows.
Key Purposes of Ceramic Filters
Removing Impurities: Ceramic filters catch solid bits in the liquid metal. This gives you cleaner aluminum. It makes the final cast stronger and cuts down on hidden flaws.
Stopping Rough Flow: These filters calm the metal flow. A calmer flow means less turbulence. This reduces the chance of oxides forming and protects the mold from wearing down. I believe this is vital for keeping your product quality high.
Quantified Benefits
Less Scrap: When you add ceramic foam filters to your production line, you will see lower reject rates. This is because there are fewer defects. Foundries I’ve worked with report big savings from less waste and lower running costs.
Better Surface and Easier Machining: I’ve noticed that castings made with these filters have a much smoother surface. They don’t need as much polishing later. They are also easier to machine. As a result, your tools last longer, and you spend less on maintenance.
Consistent Results: I recommend filters with a uniform cell structure. They provide the same filtering ability every time. This means you can expect the same high quality with every batch.
Technical Features and Customization Options
Heat and Material Tolerance: Standard aluminum casting filters (Al2O3) can handle temperatures from 820°C to 1000°C. Other ceramic types can go as high as 1700°C, which I find very impressive.
Custom Filtering: You can get filters with different pore sizes, from 10 PPI to 30 PPI, Some filters can go up to 60 PPI or 80 PPI. I suggest you choose based on the flow rate and cleaning level you need.
Pouring and Flow Details: Normal use involves pouring temperatures up to 1470°C and pour times up to 60 seconds. Labs test how well liquid flows through different grades (like 30, 50, and 80 PPI). This data helps you pick the right filter for your specific metal and production needs.
Industry Adoption
Used in Many Industries: I see ceramic filters used everywhere now. They are essential in the car, aerospace, and other foundry industries. They help make high-quality metal parts without defects.
Custom Options: You can get filters in standard or custom shapes and sizes. This gives you flexible options that can fit your specific casting setup.
Practical User Benefits
- You will see a clear drop in impurities in your final product, which means less rework.
- You get fewer scrapped parts and fewer customer returns.
- Your production runs faster because you won’t need to repair molds as often.
- You will lower your quality control expenses and total production costs.
- You can increase your output because the metal flow is stable and reliable.
In my opinion, ceramic filters are now the standard for filtering liquid aluminum. They perform well technically and are a smart financial choice. They help you meet today’s high demands for production and quality.
Types of Ceramic Filters for Aluminum Casting
For aluminum casting, you have a few choices for ceramic filters. Each type helps you meet specific needs and quality targets. From my experience, ceramic foam filters are the most common and effective choice. Alumina-based filters are a great starting point. You can also find advanced filters for special alloys and tough processes.
Main Types of Ceramic Filters
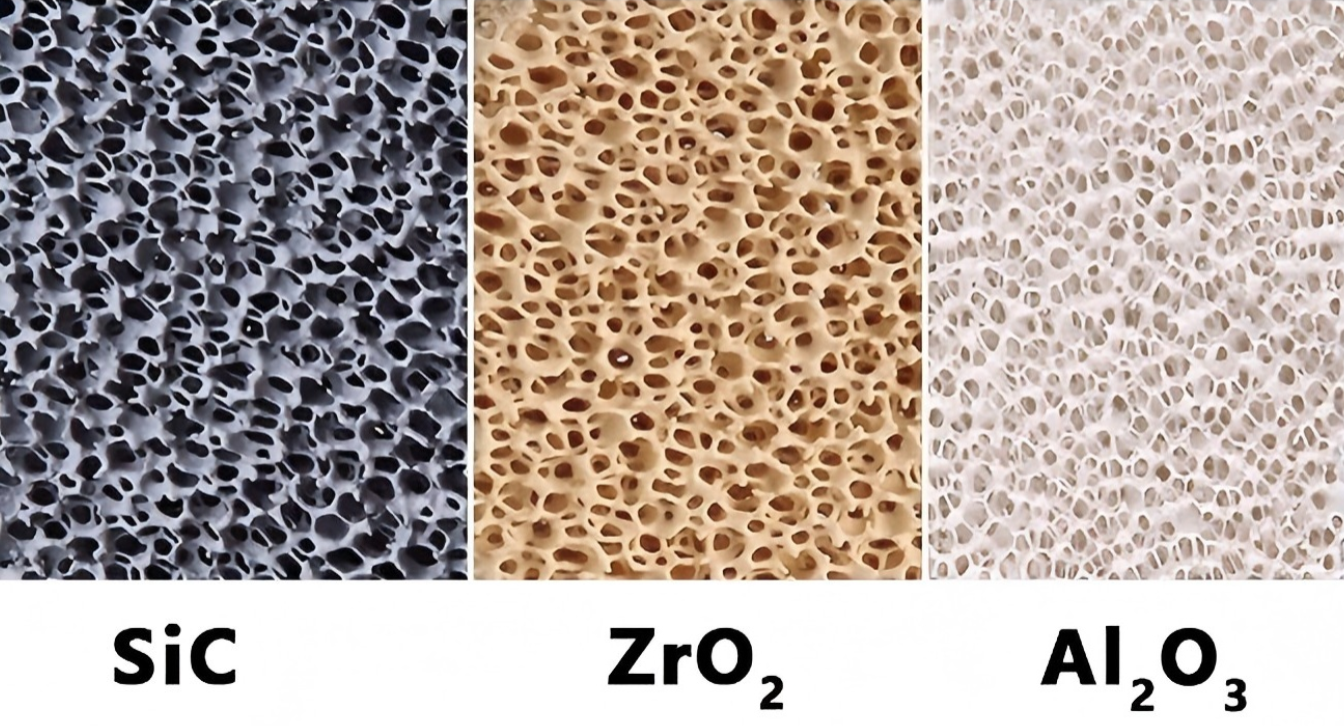
Ceramic Foam Filters (Alumina-Based)
This is the most popular filter in aluminum foundries. I like its high porosity (80–90%). This lets metal flow through quickly and removes impurities well. Its compressive strength is ≥0.8 MPa. Many filters go up to 1.0 MPa at room temperature. It works at temperatures up to 1200°C. This is perfect for almost any aluminum casting job. The bulk density is in the 0.36–0.50 g/cm³ range.
Silicon Carbide (SiC) Foam Filters
I suggest these for high-temperature alloys. They also work well with aluminum alloys that react with other materials. They can handle temperatures up to 1450°C. They resist thermal shock better and last longer in tough conditions.
I pick these for work at very high temperatures (up to 1700°C). You won’t see them as often in standard aluminum foundries. They are used mostly for special alloy or metal processes. These jobs push heat and chemical resistance to the maximum.
Key Technical Details of Ceramic Filters for Aluminum Casting
From my experience, ceramic filters in aluminum casting must be tough. They handle high heat and give precise filtration. Here are the key technical points I think you should know.
Standard Dimensions and Customization
- Standard Sizes: You can find these in many inch sizes, like 7×7, 9×9, 12×12, up to 26×26 inches. Metric sizes are also available, from 178×178 mm to 660×660 mm.
- Typical Thickness: The most common thickness I see is 50 mm.
- You can use Filter boxes and expansion seals to easily fit them into modern casting setups.
- Custom options: In my opinion, it’s worth asking suppliers for custom filters. Many can make them to your exact size, shape, and installation needs.
Filter Pore Options: (PPI – Pores Per Inch)
- Options pore sizes include 10, 20, 30, 40, 50, and 60 PPI.
- Standard aluminum casting: I recommend 10–40 PPI. This gives a good mix of flow rate and impurity removal.
- Aviation or high-end alloys: For these, I suggest 30–60 PPI. This offers finer filtering for very pure results.
- When you choose a PPI, you should think about the alloy type, how complex the casting is, and what defects you need to get rid of.
The demand for better, defect-free aluminum is growing. From my perspective, this is why more foundries are using advanced filter technologies. They are also moving to designs with tighter tolerances.
Based on my experience, if you understand and match these technical details, you can pick the right filter. This will help you improve product quality, cut down on waste, and meet the tough demands of the aluminum casting industry.
Application Scenarios
If you make standard aluminum parts, I’d use a lower PPI to get the fastest flow. If you are an aerospace or premium alloy caster, you should use higher PPI filters. This helps remove the smallest particles and improves the final product’s strength. You can add filters at different points in the casting system. Based on my experience, placing them closer to the mold entrance gives you the best control over impurities.
Industry Standards and Advanced Solutions
You can get both standard and custom shapes and sizes, which support most foundry processes. They use high-performance alumina ceramic foam filters. Their manufacturing controls are strict, and they support rolling, forging, and extrusion work.
Summary Table: Typical Properties of Alumina Foam Filters
| Property | Typical Value |
|---|---|
| Porosity | 80–90% |
| Compressive strength | ≥0.8 MPa (up to 1.0 MPa) |
| Bulk density | 0.36–0.50 g/cm³ |
| Working temperature | ≤1200°C |
| Common pore size (PPI) | 10–60 |
| Main applications | Aluminum & its alloys |
| Key materials | Alumina, SiC, ZrO₂ |
To sum it up, I believe alumina-based ceramic foam filters are the top choice for filtering aluminum. They offer a great combination of fast flow, strength, chemical resistance, and value. If you work with special alloys or in extreme conditions, I suggest looking at SiC and ZrO₂ filters for better performance. Always match the filter type and pore size to your specific alloy, project, and quality goals.
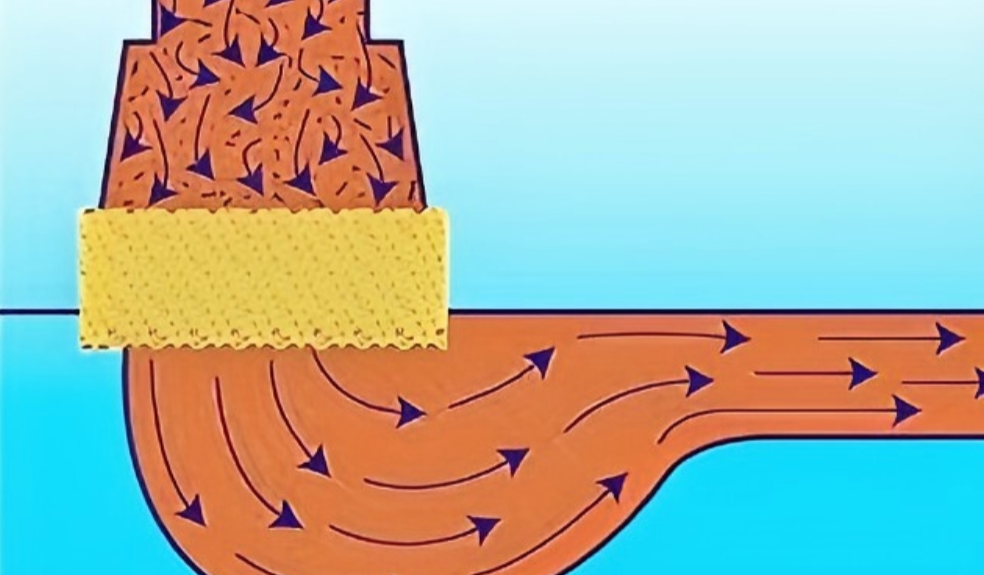
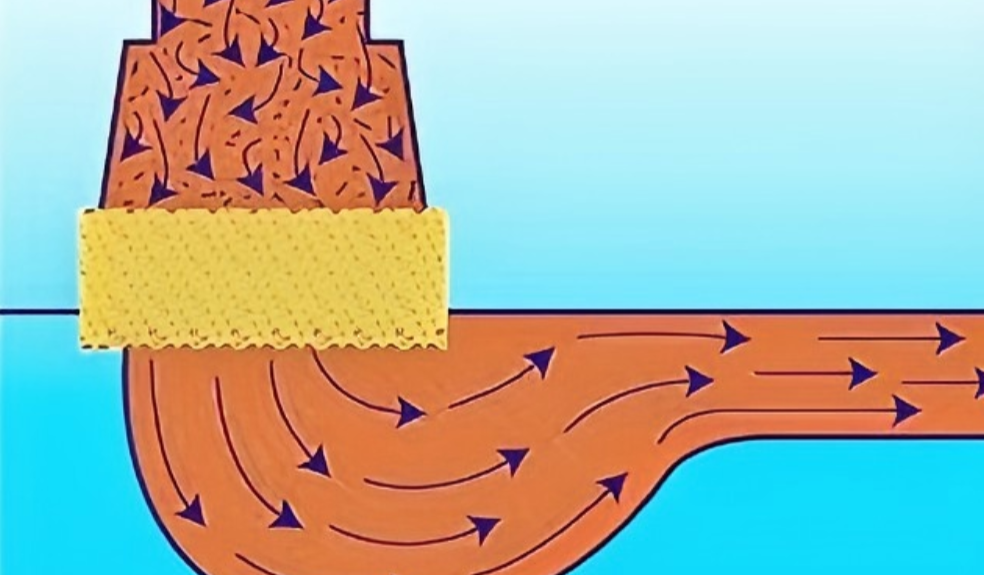
How Aluminum Casting Filters Work
Ceramic foam filters use several methods to remove unwanted particles and impurities from the molten metal. These methods work together, leading to higher purity and better quality in your final castings.
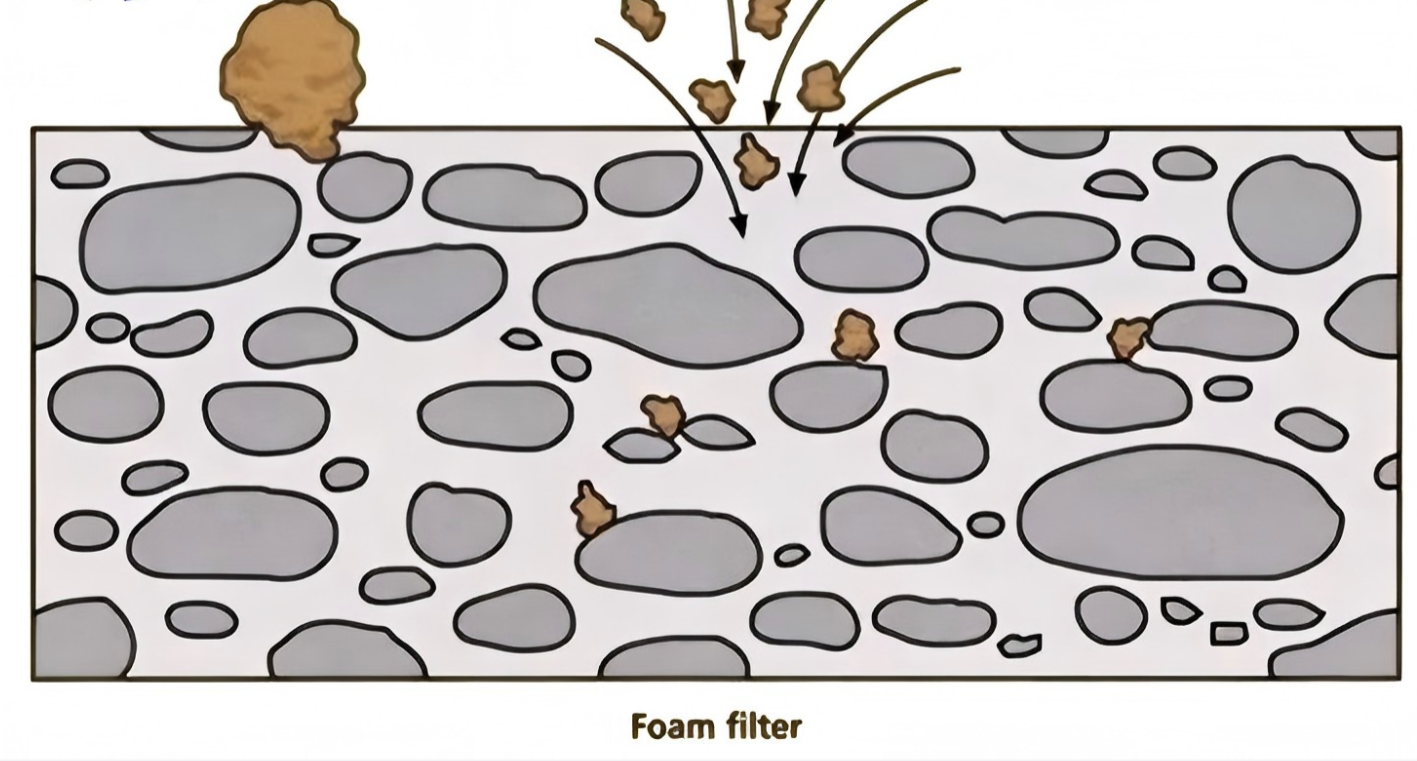
Screening: Think of this as a simple sieve. The filter’s matrix directly blocks large particles as the molten aluminum flows through. This creates what we call a “filter cake”—a layer of trapped debris. I’ve found this cake actually improves filtration, capturing even smaller particles as more metal flows past.
Deep Filtration & Sticking: The filter has a 3D, maze-like structure with 80%-90% open space. As liquid aluminum travels this winding path, small impurities are forced to change direction. This causes them to slow down and stick to the ceramic walls. The large internal surface area is what makes it so good at purifying the metal.
Calming the Flow & Separation: The filter also acts to calm the metal flow. It splits the main flow into smaller, slower streams. This reduction in turbulence (a lower Reynolds number) is important. It allows fine impurities and slag to float to the surface and out of the main metal stream, which helps prevent casting defects.
Removing Scum: The filter also directs larger pieces of scum or dross. It steers them away from the metal flow, allowing them to be separated more easily. This is another way it reduces impurities.
Static Cling for Tiny Particles: The filter’s surface has tiny pits, about 1–10 μm in size. I think of these areas as using static cling. They use small electrostatic forces and micro-adhesion to trap the very smallest impurities. This small detail greatly increases the filter’s overall effectiveness.
From my perspective, ceramic foam filters provide an effective, multi-step barrier that is essential for anyone aiming to produce clean and high-quality aluminum.
Using Ceramic Filters in the Aluminum Casting Industry
Major Industrial Sectors Using Ceramic Filters
Automotive Manufacturing: For making cars and trucks, I find ceramic foam filters are vital. They help create lightweight, strong aluminum parts. This improves fuel economy and meets tough quality rules.
Aerospace Components: Aerospace companies need perfect, high-strength aluminum alloys. I recommend advanced ceramic filters for these needs. Some use nanotechnology to remove tiny particles from engine parts and other critical components.
Electronics Manufacturing: In electronics, high-purity ceramic foam filters (>99.6% purity) see wide use. They are used to make semiconductors and other precise electronic parts. Today, the electronics industry is the biggest market for these filters. Even the smallest impurity can ruin performance, so I think their use here is justified.
The use of automation and robotics in filter making helps improve quality control. It also meets the high production demands of foundries around the world.
I believe ceramic filters are now a standard part of the automotive, aerospace, electronics, and chemical industries. Their importance is growing. This is due to tougher quality demands, the need for more output, and advances in metal casting tech globally.
summary
Based on my years of experience, these filters have completely changed how we ensure aluminum casting quality. The technology keeps improving, and I am excited to see what comes next. I believe if you want to produce top-grade aluminum parts, ceramic filters are essential. In my view, they are not just an option. Investing in the right filtration system builds your reputation and also secures the trust of your customers.