Sourcing ceramic filters from China shifts your profit margins. Whether you run a foundry needing Foam Filters for molten metal or a tile plant seeking precision cartridges, you see the benefit. Bulk pricing often sits between $0.40 and $1.00 per unit. That cost advantage makes sense. But importing fragile tech components poses challenges. It takes more than just picking the cheapest supplier on Alibaba.
The risks are real. You face strict heavy metal leaching standards in the US and EU. Plus, your shipment must survive a 40-day ocean journey without cracking. You have zero room for error. Also, consider the recent 2025 export controls on rare earth elements. Customs clearance is now a tougher hurdle that surprises many importers.
We explain the practical steps here. We won’t just list product types. Instead, we walk you through vetting suppliers and getting solid lab reports. You also learn to manage the documentation. This gets your goods out of the port and onto your production line safely.
Product Identification and Specifications
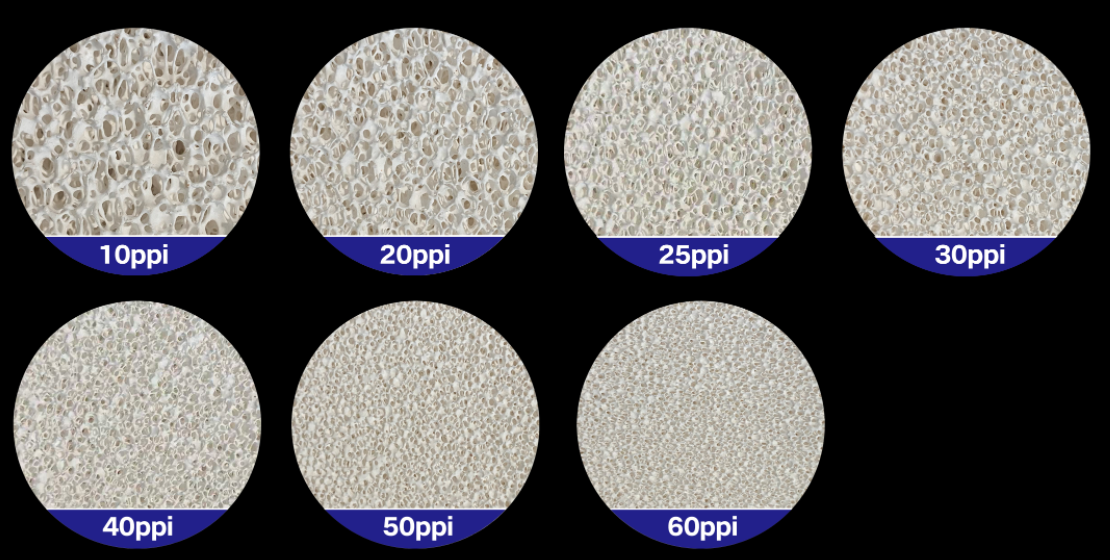
Ceramic filters come in six main types: foam, pot, membrane, roller, cartridge, and disc. Each type works for different industrial uses.
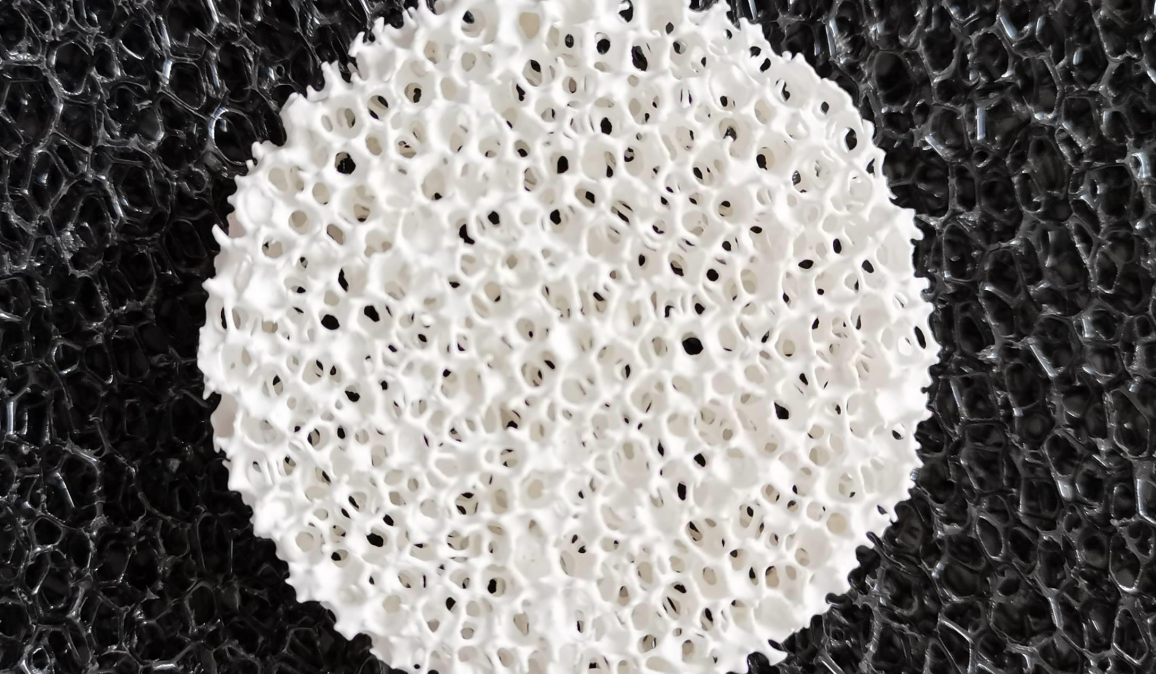
Foam filters for Molten Metal
These foam filters are the top choice for Metal casting. The chemical makeup contains 83–86% alumina and 6–7% silicon dioxide. They work at temperatures up to 1100°C. Standard sizes are 30×30×5 cm blocks. You use them to filter molten metals during casting. This removes impurities and gives you better final product quality.
Cartridge and specialty filters
Cartridge filters work on ceramic tile production lines. They come in different precision levels. Model 9680100025 gives you 10 μm filtration. Model 9680100026 provides 20 μm filtration. Filtration ratings range from 10 μm to 40 mesh. The range depends on what you need.
Enamel filters measure 104×190 mm. They use stainless steel construction. You’ll find them in ceramic tile enamel coating processes. Ink filter DA32340 has a 10 μm rating. It’s built for tile production operations.
HS Code Classification
Correct classification helps you clear customs smoothly:- US Code: 6909.19.5095 (ceramic wares for technical uses)- China Code: 69039000.00 (ceramic foam filters)- Global Code: 84212990 (for ceramic and tile production equipment)
Check compliance with your destination market standards. FDA and EU rules control heavy metals. Lead content limits are:
– Flatware: 3.0 ppm max
– Small hollowware: 2.0 ppm max
– Large hollowware: 1.0 ppm max
– Children’s items: 0.5 ppm max
You must complete testing and get certification.
Supplier Search and Evaluation
Three B2B platforms offer the most supplier choices: Alibaba, Made-in-China, and Global Sources. Trade data providers like Volza and Import Genius give you access to real shipment records. You’ll see exporter names, import volumes, and bill of lading details from actual deals.
Essential Supplier Information to Collect
Build your supplier database with these core parts:
-
Full company name, verified address, and direct contact methods (phone, email, WeChat, WhatsApp)
-
Export history with shipment dates, overseas buyers, and volume patterns (typical range: 50–1800 units per invoice based on Volza records)
-
Third-party buyer references or published client lists
-
Quality certifications: ISO 9001, CE, FDA, SGS
-
Lab test reports with product makeup (83–86% alumina, 6–7% SiO2, maximum temperature 1100°C)
-
Product labels showing country of origin, maker name, material content, and safety warnings
Price Benchmarking from Real Shipments
Bill of lading data from 2024 shows bulk pricing for Foam ceramic filters (30×30×5 cm) ranges from $0.40 to $1.00 per unit. Shipment sizes differ widely. Small orders start at 13 pieces ($197.34 total). Large batches reach 1,800 pieces ($4,320 total).
Shipment patterns on multiple dates each month show rolling production capacity. Guangzhou Haoqi shipped 50-piece cartridge filter orders (Model 9680100025, 10 microns) to Vietnam for $590.50 in September 2024. Foshan suppliers handled smaller 13-piece orders of Model 9620200051 for $197.34 to the same market.
Seven-Step Evaluation Process
Follow this sequence to check supplier reliability:
-
Search ceramic filter suppliers across B2B platforms and trade databases
-
Pull supplier details that show clear export performance
-
Check that certifications match your target market needs
-
Ask for recent buyer references from their trade partner list
-
Get samples with detailed makeup data and certified test reports
-
Compare unit pricing, MOQs, lead times, and payment terms from at least three suppliers
-
Place a trial order to test quality standards and delivery reliability before you scale up
How fast suppliers respond and how complete their documents are during first contact shows their professionalism.
Regulatory Compliance and Quality Control
Lab testing is your first step for importing ceramic filters from China. Each shipment needs test reports from accredited labs. Customs won’t clear your products without these. Take three product samples and ship them to recognized testing facilities. The reports confirm heavy metal levels stay within legal limits.
Heavy Metal Testing Standards
Ceramic filters must meet strict leaching limits in major markets. The US FDA sets these maximum levels for food-contact ceramics:
-
Flatware: 3.0 ppm lead maximum
-
Small hollowware: 2.0 ppm lead maximum
-
Large hollowware: 1.0 ppm lead maximum
-
Children’s items: 0.5 ppm lead maximum
EU markets apply Ceramic Directive 84/500/EEC for toxic element leaching. You need CE marking on your products. They must also meet EN 1388 and EN 1184 standards. India has different rules. Get approval from the Ministry of Environment and Forests (MOEF) before importing ceramic products there.
Documentation and Labeling Requirements
Each product label must show:
-
Country of origin (China)
-
Manufacturer ID number
-
Material makeup
-
Care and handling instructions
-
Safety warnings for intended use
-
Compliance marks (CE for Europe, FDA registration number for US)
Missing labels mean customs seizure and penalty fees. Keep valid Certificates of Origin with your lab reports. No documents? Your shipment gets detained or sent back to China.
Record Retention and Compliance Audits
Keep all test reports and certificates for at least two years. Agencies run random audits. Can’t show documents during inspection? Your past import compliance means nothing.
Shipments that fail tests go back within 90 days. Hazardous waste rules apply here. This happens if products show too much lead or cadmium after arrival testing.
Order Placement and Contracts
Your purchase order locks in every detail of the ceramic filter deal. Write the exact quantity—”10,000 ceramic filters.” No approximate numbers. Add product specs: dimensions, filtration precision (like 0.1 micron), material grade, and packaging needs. State the unit price and total price in clear currency (USD or RMB).
Pick your INCOTERMS with care. FOB Shanghai?
Production and Packing
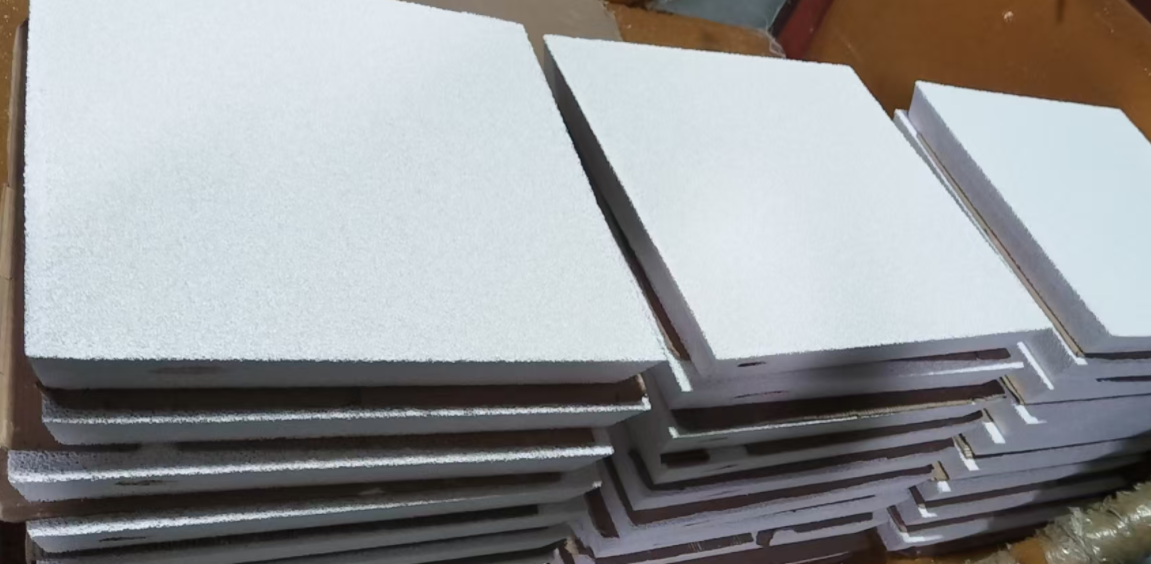
Standard production takes 30 to 120 days before your ceramic filters ship from China. Lead time depends on three things: order size, product complexity, and your supplier’s production queue. Foam filters in standard 30×30×5 cm blocks get done faster. Custom cartridge filters with special micron ratings take longer.
Export Packaging Standards
Strong packaging protects your shipment during ocean transport. Suppliers use materials that resist salt air, temperature changes, and humidity for 20–40 days at sea. Ceramic filters break fast. Wrap each piece in foam sheets or bubble wrap first. Then pack them into strong cartons. Outer boxes need strapping and corner guards for safe container stacking.
Required Package Markings
Every shipping carton needs clear labels with:
-
Country of origin: “Made in China”
-
Manufacturer name and contact details
-
Material makeup (example: 85% alumina, 6% SiO2)
-
Handling symbols (Fragile, This Side Up, Keep Dry)
-
Product model numbers and quantities inside
-
Gross weight and net weight in kilograms
-
CE marking if you’re shipping to European buyers
Wrong labels slow down customs. Inspectors check every mark against your invoice and packing list. Ask for samples of your supplier’s export cartons before production starts. This way you confirm the packaging fits your country’s import rules.
Shipping Process and Logistics
Pick your shipping method based on order size and how fast you need it. Full Container Load (FCL), Less than Container Load (LCL), or air freight – each fits different needs.
Ocean freight FCL works best for shipments over 10 cubic meters or 15,000 kg. LCL costs less for smaller volumes. But it adds 3–5 days at the port for consolidation. Air cargo runs 5–8 times more expensive than sea transport. The upside? Transit drops to 5–7 days versus 20–40 days by ocean.
Timeline Breakdown for Ocean Shipments
Your supplier kicks off production 30–120 days before the ship leaves. Track these key milestones:
-
T-120 to T-30: Pay your deposit (usually 30% of total value). Confirm production start.
-
T-15 to T-12: Book pre-shipment inspection with SGS or Bureau Veritas.
-
T-10 to T-7: Wire the balance payment (remaining 70%) after inspection passes.
-
T-8 to T-6: Finish packing with export-grade materials. Seal everything up.
-
T-8: Request empty container delivery to factory.
-
T-6 to T-4: Load and seal container.
-
T-4 to T-3: File export customs declaration with Chinese authorities.
-
T-2 to T-0: Get customs clearance. Move container to port terminal.
Export Customs Documentation
Your freight forwarder needs these papers 4 days before shipping:
-
Commercial invoice with correct HS codes (6909.19.5095 or 69039000.00)
-
Packing list showing carton count, dimensions, and weights
-
Lab test reports proving you meet FDA or CE standards
-
Product photos, labels, and handling instructions
-
Certificate of Origin if your country needs it for duty preference
Missing documents delay the ship’s departure. You’ll face demurrage charges of $100–300 per day.
Key Shipping Documentation
Seven core documents decide if your ceramic filter shipment clears customs or gets stuck in detention. Each paper has a specific legal purpose. Miss one document? You pay $100–300 per day in storage fees while containers sit at port.
Bill of Lading (B/L)
This document proves you own the cargo. It confirms the shipping line received your goods. The ocean carrier gives you one after loading containers onto the ship. You need the original B/L to claim your shipment at destination. Keep it safe—no B/L means no cargo release.
Commercial Invoice and Packing List
Your commercial invoice shows product values, quantities, and full descriptions. Customs uses these numbers to calculate import duties. The packing list breaks down box counts, weights, and what’s inside each pallet. Your actual shipment must match these details. One box off? Customs delays your entire shipment.
Certificate of Origin (CoO)
This certificate states “Made in China” as an official record. Many countries need it to set correct tax rates or trade agreements. Some buyers need it for lower duty rates under free trade deals.
Certificate of Analysis and Test Reports
The Certificate of Analysis shows filter makeup—alumina percentage, silicon dioxide content, top working temperature. Test certificates prove your products meet FDA heavy metal limits or CE safety rules. Customs in strict markets won’t clear shipments without these lab proofs.
Document Delivery Timeline
Suppliers send all paperwork via DHL, FedEx, or UPS within 3–5 working days after the ship leaves port. You get documents before your vessel reaches destination. This head start gives you time to prepare customs forms and line up clearance agents. Late documents create problems—your containers arrive before paperwork. Customs won’t touch anything until all papers reach you.
Import Customs Clearance & Delivery
Customs clearance takes 2–4 days once your shipment hits port with clean paperwork. This works for standard ceramic filters without controlled materials. On December 1, 2025, new rare earth rules changed the game for certain products. Got filters with even tiny amounts of rare earth elements? Processing time shoots up to several weeks.
Rare Earth Export License Requirements
China’s Ministry of Commerce (MOFCOM) now controls ceramic filter exports containing any rare earth content. The watch list covers these elements: neodymium, dysprosium, terbium, samarium, praseodymium, yttrium, and scandium. Your supplier needs MOFCOM approval before shipping. No license? Customs grabs your goods at departure. Or they block them at your destination.
The 50% rule bites hard. Your company or end-user appears on China’s export control entity list? Import authorities deny licenses on the spot. A listed entity owns 50% or more of your business? Same denial.
Controlled ceramic materials use these HS codes: 3824999922, 8486909110, and 2846901600–2846909920. Dual-use items under MOFCOM notifications 18, 56, 57, 58, or 62 from 2025 trigger reviews from multiple agencies. Clearance takes longer than usual.
Arrival Inspection Protocol
Unpack containers right after customs releases them. Check every carton against your packing list. Count pieces. Look for cracks, chips, or water damage. Snap photos of any problems fast. File claims with your freight carrier and local customs office within 24 hours. Wait too long? You lose your right to get paid back.
Some customs agencies pull random samples for rare earth testing. Budget extra days if inspectors flag your shipment for lab work.
Market Data and Trends (Optional for
Risk Mitigation and Success Tips
Key Contacts & Resources
Build your support network before you place orders. Call China’s General Administration of Customs at +86-10-65194114 for HS code checks and licensing help. The US International Trade Administration at trade.gov/china gives you free market briefings. They also help vet suppliers for American importers.
Essential Professional Services
Hire customs brokers who work with ceramic imports every day. They handle your entry documents, figure out duties, and take care of FDA or CE compliance forms. Freight forwarders book your container shipping, track vessels, and set up port pickups. Testing labs like SGS (sgs.com) and Bureau Veritas (bureauveritas.com) run pre-shipment inspections. They also test for heavy metals.
Industry groups give you solid resources. Try the Ceramic Tile Distributors Association or China Chamber of Commerce for Import and Export of Machinery and Electronic Products. Members get supplier directories, attend trade missions, and receive regulatory updates. LinkedIn groups for ceramic importers share real supplier stories. You’ll find shipping problem fixes there too.
Trade databases track shipments and help you find new exporters. Volza, Panjiva, and ImportGenius work well for this. Set alerts for ceramic filter HS codes. This helps you watch competitor activity and spot pricing trends.
Common Problems & Solutions
Delays affect most first-time ceramic filter importers from China. Keep safety stock that covers 10–15% of your monthly needs. This buffer protects your production line from late shipments. Lead time from order to delivery takes 25–40 days on average. One shipment of 1,800 foam ceramic filters (30×30×5 cm) from China to Vietnam took 32 days in 2024.
Add penalty clauses for late deliveries. Put specific dollar amounts in your contract. “Supplier pays $100 per day after agreed ship date” beats vague terms. Missed deadlines cost you money—make them cost your supplier too.
Quality Control That Works
Pre-shipment inspection catches problems before containers leave China. Hire SGS or Bureau Veritas to check your order. Set your Acceptable Quality Level at 2.5 for major defects. Set it at 4.0 for minor ones. Guangzhou Haoqi’s cartridge filters passed third-party inspection this way. They got 100% new units, 10 micron filtration confirmed, and chemical makeup verified.
Ask for lab certificates showing alumina content between 83–86%. Check for silicon dioxide at 6–7% for foam filters. Run random batch tests after arrival. Match supplier data against your own results. Food-contact ceramics need closer checks. Test every shipment for lead leaching. Stay within these limits: flatware under 3.0 ppm, small hollowware under 2.0 ppm, large items under 1.0 ppm, children’s products under 0.5 ppm.
Documentation Mistakes That Trigger Customs Holds
Wrong HS codes cause duty errors and clearance delays. Check classification before shipping. Use 69039000.00 for Ceramic foam filters. Use 84212990 for industrial cartridge types. One importer paid 4% extra duty on foam filters. Documents listed the wrong HTSUS code (6909.19.5095).
Check every paper item by item. Commercial invoice must match packing list. Bill of lading should show correct quantities. Certificate of origin must state China. Test reports need to cover all required standards. Missing compliance certificates freeze shipments at port. One molten copper filter order sat in customs for seven days. The importer had to rush environment clearance documents and lab reports to release it.