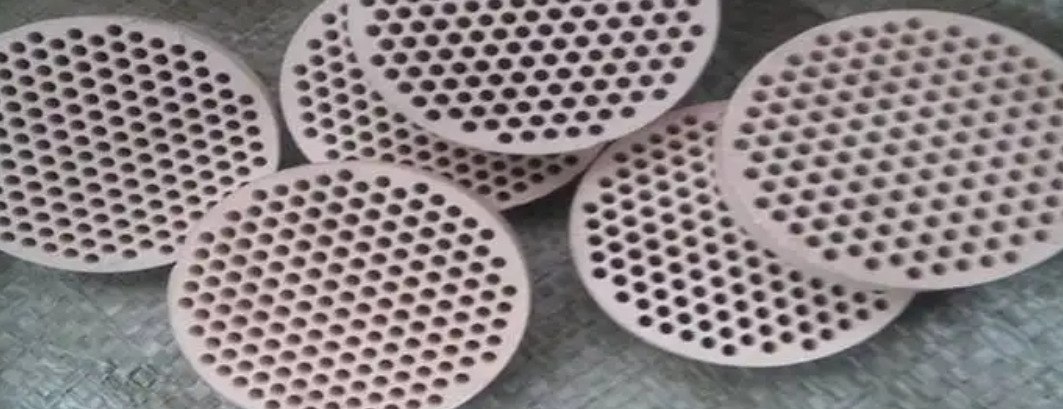
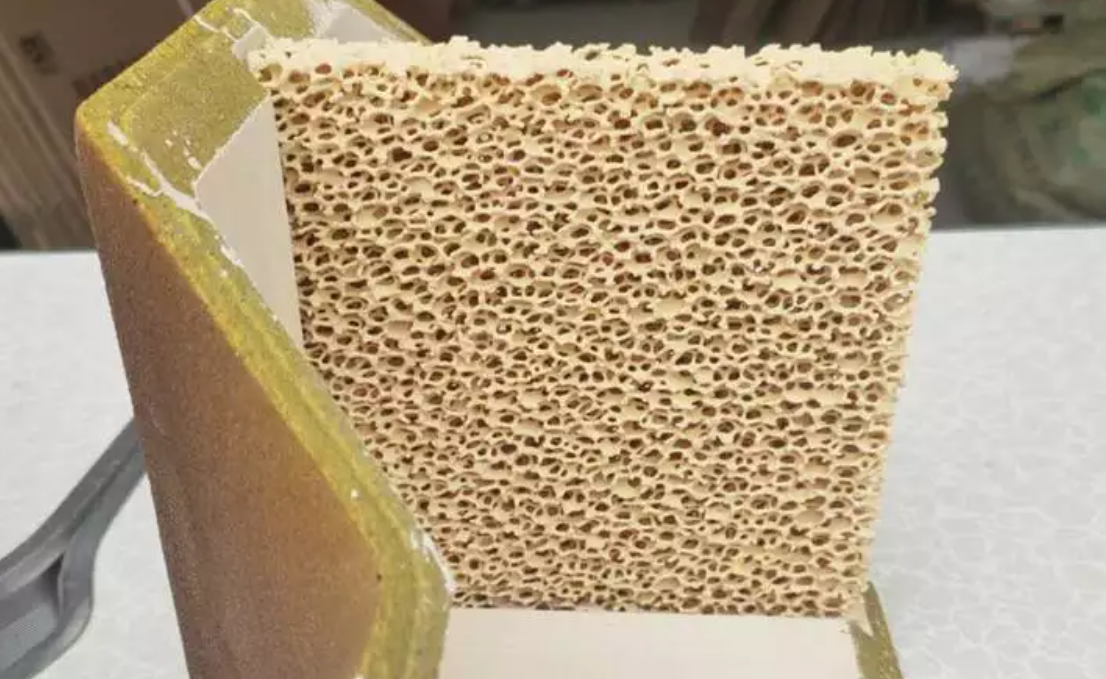
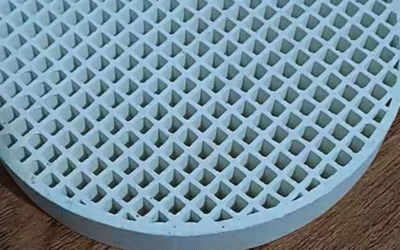
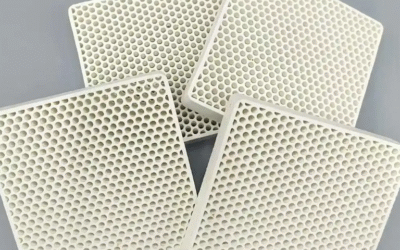
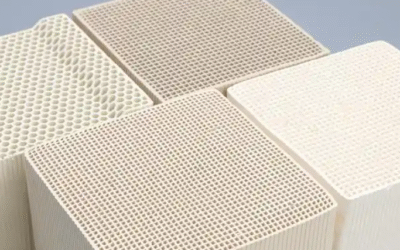
The right honeycomb filter makes or breaks your foundry’s metal casting quality. But dozens of suppliers across China claim they’re the best. So how do you spot real performance versus marketing hype?
You might be fighting inclusion defects in aluminum castings. Or maybe you need better filtration for your production line. Either way, your ceramic honeycomb filter choice affects your yield rates and product quality.
China’s foundry filtration market has changed a lot. Specialized makers now offer silicon carbide types and advanced extruded ceramic designs. This guide evaluates the 5 best honeycomb filter suppliers for foundry applications in China. We examine their core technologies, performance numbers, and real-world reliability.
You’ll learn which makers handle thermal shock resistance best. We show how different ceramic materials affect filtration precision. Plus, you get practical selection tips that match your specific casting needs. This helps you make a smart choice that protects your casting quality and saves money.
FoundryMax – Extruded Ceramic Filter Specialist
FoundryMax facility makes ceramic filters for foundries. We handle everything from basic aluminum work to extreme steel casting. Our three-tier system uses Alumina, Silicon Carbide (SiC), and Zirconia. These materials cover the full temperature range from 1000°C to 1700°C.
Material-Specific Temperature Performance
Alumina filters work at 1000°C for aluminum ingot and billet casting. They resist softening up to 1390°C. Compression strength reaches ≥12 MPa. That’s enough for standard gravity pouring systems. These filters target aluminum alloy purification. Lower melting points don’t stress the ceramic structure.
Silicon Carbide filters handle working temperatures up to 1550°C. Compression strength goes up to ≥15 MPa. This handles higher back-pressure in copper, ductile iron, and gray cast iron jobs. SiC material fights off chemical attack from molten metals better than alumina grades. It works for both ferrous and non-ferrous applications.
Zirconia ceramic foam filters reach the highest temperature at 1700°C maximum. Steel casting needs this type. High-alloyed and stainless grades would damage other materials. FoundryMax uses zirconia for the toughest steel foundry jobs.
Thermal Expansion Control
Controlled expansion gives you thermal shock resistance. Our mullite-based honeycomb structures keep expansion below 1.8 x 10⁻⁶/°C. Other ceramic types stay under 4.0 x 10⁻⁶/°C. This tight control stops cracks from forming. Temperature changes happen fast in automated pouring systems.
Shape Flexibility and Order Requirements
You get standard shapes: square, rectangular, and round. Custom designs fit non-standard launder shapes. Size options include 6″, 7″, 17″, 20″, 23″, and 24″ diameter plates. Different PPI ratings are available.
Volume requirements matter here. Minimum order is 1000 pieces per product type. This applies to honeycomb extruded, SiC foam, and specialty formats. Mid-to-large foundries can handle this MOQ. Small-batch operations or testing facilities might find this too high for filtration upgrades.
SEFU Ceramic – High Thermal Shock Resistant Honeycomb Ceramic Filter
SEFU Ceramic’s thermal shock resistant honeycomb filters solve a major foundry problem: sudden temperature changes that crack standard ceramic filters. The high thermal shock stability design stops filter failure during fast heating cycles and emergency production changes.
Thermal Shock Engineering
SEFU’s thermal stability relies on controlled ceramic grain structure. Standard honeycomb filters crack during foundry work. Restarting cooling ladles causes cracks. Switching between different alloy types causes cracks. SEFU’s material spreads internal stress to handle temperature changes. You can move filters from room temperature storage into 1450°C molten aluminum right away. No pre-heating needed. This keeps production moving fast.
Best Applications for High Thermal Shock Filters
Automated foundry lines gain the most from SEFU’s thermal shock resistant honeycomb filters. Robotic pouring systems move through multiple temperature zones each shift. Traditional ceramic filters need replacement after 3-4 thermal cycles. SEFU’s design lasts 8-12 cycles before breaking down.
Batch casting operations benefit from mixed production schedules. A foundry switches from 680°C aluminum alloy to 760°C bronze in one day. This puts huge stress on filter materials. The thermal expansion stays stable across these temperature swings. This stops micro-cracking. Micro-cracks let unwanted particles slip through filtration zones.
Integration with Existing SEFU Systems
These thermal shock resistant units fit SEFU’s standard 35-200mm square and round formats. The same 50/100/200/300 CSI pore density options work here. Physical mounting systems stay the same. No changes needed. Just specify the thermal shock resistant grade at ordering. The oxide removal feature stays active. You get dual-action filtration performance plus temperature cycle strength.
ADTECH Metallurgical Materials – Foam Ceramic for Aluminum Melt Purification
ADTECH Metallurgical Materials leads China’s aluminum melt purification market. They produce at massive scale using U.S.-licensed technology. They make 400,000 ceramic filter plates each year. These plates go to foundries in rail transit, automotive, military aviation, and electronics. High-demand production schedules? They keep supply steady.
Market Leadership in Degassing Equipment
ADTECH holds over 20% of China’s market for precision online degassing filtration equipment. They build 40 complete units each year. Each unit combines our foam ceramic filters with active degassing chambers. This setup delivers purification and degassing efficiency above 60%. Aerospace-grade aluminum needs hydrogen porosity below 0.05 ml/100g. Their systems hit that mark.
Three-Dimensional Network Manufacturing Process
They build their foam ceramic structure using a different method than extruded honeycomb types. First, They use an organic foam carrier to create the base shape. Then they dip the carrier in special refractory slurry. Their four-way correction center distance automatic extrusion technology handles the coating. What do you get? Even coating thickness on all internal struts with connected pores throughout the network.
This method creates more surface area than parallel-channel honeycomb designs. More surface contact means better adsorption of oxide particles and inclusion clusters. The connected pore structure catches contaminants two ways: mechanical straining and chemical adsorption.
High-Precision Deep Processing Applications
Their foam ceramic filters handle precision aluminum deep processing needs. Rail transit parts need zero defects to pass safety checks. Automotive engine blocks need steady microstructure for tight machining. Military and aviation parts must clear X-ray inspection. Solar frames need corrosion resistance, which depends on low inclusion counts.
Their filters pair strong ceramic bodies with sharp filtration accuracy at good prices. U.S. technology licensing gives them access to advanced refractory formulas. You pay less than imported filters. Plus, you get the same international-grade purification.
SF-Foundry – Ceramic Honeycomb Filters
SF-Foundry makes ceramic honeycomb filters using a special foam replication process. This method is different from standard extrusion. They start with reticulated polyurethane foam as the base template. The foam needs a uniform mesh structure. It also needs good water absorption and high bounce-back ability. These traits help create consistent pore networks.
Advanced Slurry Formulation Technology
The ceramic slurry uses high-temperature alumina as the main raw material. Material mix includes 20-50% SiC and 20-55% ZrO₂ by weight. The exact ratio depends on how hot your application runs. SF-Foundry combines heat-resistant aggregates with sintering aids. They add special binders, fine powders, and the right amount of water.
Their binder system is unique. It combines potassium salt treated with phosphoric acid, aluminum-chromophosphate binder, aluminum hydroxide, and ceramic waste as filler. Water content is 40-55 parts per binder portion. Slurry density stays between 1.8-2.2 g/cm³. Solid content is 50-65%. They mix for 30-40 minutes to get everything completely even.
Five-Stage Manufacturing Process
Stage 1 – Foam Preparation: Cut polyurethane foam to exact sizes. Each piece has uniform mesh all the way through.
Stage 2 – Impregnation: Dip the foam template into prepared slurry. Then squeeze out extra material. This controls the final wall thickness. It also stops pores from getting plugged.
Stage 3 – Green Body Drying: Low-temperature drying takes out free water first. Room temperature air drying comes next. Hot air treatment finishes the job and removes all moisture.
Stage 4 – Controlled Firing: Temperature goes above the foam’s burn point. This burns off the organic template. The ceramic hardens at 1280-1290°C for standard grades. ZrO₂ filters need 1700-1800°C. SiC types fire up to 1500°C. We control heat rate carefully. This stops thermal cracks and shape changes.
Stage 5 – Slow Cooling: Temperature drops slowly. This locks in ceramic strength and keeps the exact size stable.
Filtration Performance in Ferrous Casting
SF-Foundry filters work great for cleaning ferrous metal. They use fayalite film formation. This chemical reaction layer catches tiny inclusions. It does more than just strain them out. The 3D pore network gives you lots of surface area for contact. The filters handle thermal shock and chemical attack. They work under metallostatic pressure up to 1500°C in continuous casting.
You can choose pore density from 10-45 PPI. This matches the size of inclusions you need to catch. Scrap rates drop because the filter removes dirt before it hardens into casting flaws.
NINGXIN New Materials – Silicon Carbide Suppliers
Ningxin New Materials Co., Ltd. is a specialized graphite material supplier. They don’t make silicon carbide honeycomb filters. Their 6,600-ton annual output goes into specialty graphite products and parts. They sit in a different spot in the foundry supply chain than ceramic filter makers.
Production Scale and Market Standing
Ningxin hit top three in China for specialty graphite sales during 2018-2019. Phase two expansion aims for 18,000 tons of high-purity graphite. Add 6,000 tons of lithium battery anode materials to that. Total investment hits 341 million yuan. Construction takes two years. This shows real industrial muscle. But their main work serves battery and polysilicon industries. Metal casting filtration isn’t their game.
Custom Manufacturing Capabilities
The company works on order-based production. You get customized design services. They make carbon crucibles for lithium battery anode materials. Also specialized graphite for polysilicon production. Each product needs its own molds during pressing. They outsource some steps: roasting, impregnation, and graphitization. This setup keeps things stable. Plus it controls costs.
Raw materials? They follow “produce-to-order” purchasing. Some inventory sits as buffer stock. Main materials are pitch coke, petroleum coke, medium/high-temperature pitch, and graphite semi-finished products. Quality control and cost management set them apart from trading companies.
Relevance to Foundry Filtration
Ningxin knows graphite well. But that skill doesn’t carry over to silicon carbide honeycomb filters for molten metal cleaning. No data shows foam filter strength comparison. Nothing on high-temperature oxidation resistance. Factory pricing for bulk ceramic filter orders? Missing. They don’t offer solutions for gravity casting, low-pressure casting, or die-casting that foundries want.
Their one-stop product line works better for graphite mold makers. Crucible suppliers benefit too. Looking for silicon carbide filtration systems? Check dedicated ceramic filter manufacturers. Ningxin helps foundries through graphite tooling. Not ceramic filtration products.
How to Choose the Right Honeycomb Filter for Casting Applications
Filter material controls molten metal cleaning. Match the ceramic type to your casting temperature and chemical environment. Then, check the physical dimensions and quality standards.
Material-Metal Matching Decision Table
|
Metal Type |
Recommended Material |
Working Temp (°C) |
Typical Application |
|---|---|---|---|
|
Steel / Iron |
Zirconia (ZrO₂) |
1700 |
Stainless steel, Alloy steel refining |
|
Bronze / Copper Alloys |
Silicon Carbide (SiC) |
1560 |
Copper pipes, Valve casting |
|
Aluminum Alloys |
Alumina / Mullite |
1000-1480 |
Automotive parts, Aerospace castings |
|
Magnesium Alloys |
Magnesia |
High Temp Stable |
Electronic housings, Lightweight structural parts |
Steel casting filtration demands Zirconia types. This material endures the 1700°C heat. Silicon Carbide oxidizes and fails in molten steel. Copper and Bronze display lower working temperatures, under 1560°C. Silicon Carbide resists chemical attacks here. Plus, it costs 30-40% less than Zirconia.
Aluminum alloys have lower melting points. Alumina-based filters work well for these. Magnesium alloys require Magnesia filters. This material offers lower heat capacity. It preheats fast and avoids contaminating reactive metals.
Dimensional Tolerances and Installation Fit
Common filter size ranges include:
– Round Diameter: 40-360 mm
– Thickness Options: 11-40 mm
– Standard Tolerance: ±2 mm
Measure your launder seat dimensions. Maintain tolerances within ±2 mm. Poorly made filters float loose or get stuck during installation.
The standard 80×20 mm specification fits small-to-medium batch steel refining. Large continuous casting systems need 200-360 mm diameters. Thickness controls flow rate. 11-15 mm works for high-speed automated pouring. Select 25-40 mm for long-duration continuous filtration.
Filtration Efficiency Performance Benchmarks
A high-quality honeycomb filter hits these numbers:
-
Inclusion Removal Rate: ≥95% (Oxides, flux residues)
-
Particle Capture Precision: <2.5 μm (PM2.5 level)
-
Surface Filtration Efficiency: 99-99.9% (For ultra-fine dust, inlet concentration <20 g/m³)
Ask suppliers for third-party test reports. Ensure the data includes PM2.5 particle capture testing.
Magnesium alloy casting reacts sensitive to oxide inclusions. Filtration efficiency below 95% causes porosity defects. Aerospace aluminum parts need 99%+ dust removal efficiency. This ensures they pass X-ray inspection.
5-Step Selection Checklist
-
Identify Metal Type → Steel/Copper use SiC (≤1560°C), Molten Steel uses ZrO₂ (1700°C), Aluminum uses Al₂O₃.
-
Measure Installation Spot → Verify launder diameter and keep tolerances within ±2 mm.
-
Set Efficiency Goals → Target 95% removal for standard castings, or 99%+ capture for precision parts.
-
Verify Thermal Stability → Request high-temperature thermal shock data; check thermal cycle limits.
-
Evaluate Supplier capability → Choose ISO-certified makers. Demand batch tolerance guarantees of <2 mm.
Buying in bulk? Ask for custom sizing services. Manufacturers like Baoding Ningxin handle full specs from 80-360 mm. Signing long-term contracts? Demand consistency. Every batch must meet that ≤±2 mm tolerance. This keeps your automated lines running smoothly.
Core Performance Comparison of Honeycomb Filters
Ceramic honeycomb filter performance dictates your casting quality. Look at four key dimensions: pore density, compressive strength, working temperature, and filtration precision. These specs match the filter to your process.
Pore Density (PPI) vs. Filtration Precision
We measure pore density in Pores Per Inch (PPI). Higher numbers offer finer filtration:
-
10-20 PPI: Captures large 100-300 μm inclusions. Fits the coarse filtration stage.
-
30-50 PPI: Removes 50-100 μm oxides. This covers about 80% of standard casting needs.
-
60-100 PPI: Intercepts fine 20-50 μm impurities. Key for precision castings.
-
200-400 PPI: Achieves 2-10 μm micro-particle filtration. This meets aerospace-grade requirements.
Precision ceramic’s 60-400 CSI specs capture ultra-fine particles down to 2-3 μm. SEFU’s standard series includes 50/100/200/300 CSI options. Follow this simple rule: use 30-50 PPI for aluminum die casting. Precision instruments need 100+ PPI. Casting turbine blades? Choose 200+ PPI high-density options.
Compressive Strength and Thermal Stability
Compressive strength determines survival rates under metal static pressure:
|
Strength Grade |
Compressive Strength (MPa) |
Application Scenario |
|---|---|---|
|
Standard |
8-12 |
Gravity pouring, Low-pressure casting |
|
Reinforced |
≥12-15 |
Automated lines, High-speed pouring |
|
Industrial |
≥15-20 |
Large continuous casting, Pressure die casting |
Makers like Preciseceramic and FoundryFiltration hit the ≥12-15 MPa reinforced standard. This strength withstands mechanical clamping force. Bestnpacking uses cordierite material. Its bulk density sits at 0.45-0.65 g/cm³ for fast preheating. However, its strength ranks lower than corundum-mullite types.
Operating Temperatures and Material Matching
Different ceramic materials dictate the upper temperature limit:
-
Alumina-based: Works at 1000-1480°C with a softening point of 1390-1550°C. Use for aluminum alloys.
-
Silicon Carbide (SiC): Handles 1500-1560°C. Offers chemical resistance for copper, ductile iron, and gray iron.
-
Zirconia (ZrO₂): Reaches a limit of 1700°C. The clear choice for molten steel refining.
-
Mullite/Corundum: Usable range of 1350-1700°C. Compatible with multiple metal types.
SEFU’s high thermal shock series takes direct impact from 1450°C molten aluminum without preheating. ADTECH’s foam ceramics use two processes: standard sintering at 1280-1290°C or the Zirconia process at 1700-1800°C. Always leave a 50-100°C safety margin. Pouring aluminum at 1450°C? Pick a filter with a softening point ≥1550°C.
Inclusion Removal Rates: Real Data
Tests in real production environments show clear performance gaps:
-
20 PPI Honeycomb Structure: Achieves 92-97% oxide removal rate.
-
Foam Ceramic 3D Network: Realizes 78-95% capture efficiency (for 5-80 μm particles).
-
Ultra-fine PPI (200+): Breaks through 99% particle interception (verified in aerospace grade aluminum).
Porosity defects drop by 75-85%. Flow rates improve by 30-40% compared to foam filters due to the parallel straight-channel design. ADTECH systems achieve ≥60% combined purification and degassing efficiency. This keeps hydrogen content below 0.05 ml/100g.
Dimensional Tolerances and Batch Consistency
Industrial production requires strict tolerance control:
-
Standard Tolerance: ±2 mm (across full 40-360 mm specs)
-
Custom Machining: Can reach ±1 mm (requires 3 weeks advance ordering)
-
Batch Consistency: Size deviation within the same batch <1.5 mm
Suppliers like Hebei Cangchen set a minimum order quantity of 1000 pieces/spec. This suits mass purchasing. SEFU offers the full 35-200 mm series with a 2-3 week delivery for custom sizes. Automated production lines need products with ±1 mm precision. Poor precision causes robotic arm gripping failure rates to exceed 5%.
Conclusion
The right honeycomb filter impacts your foundry’s metal quality big time. It also affects production efficiency and costs. FoundryMax offers specialized extruded ceramic solutions. NINGXIN provides high-volume silicon carbide options. Each of these 5 best honeycomb filter manufacturers in China brings unique strengths. You might need thermal shock resistance. Or maybe aluminum melt purification. Perhaps cost-effective bulk supply matters most to you.
Match filter specs to your casting needs. Check pore density for your metal type. Look at thermal stability for your operating temps. Dimensional accuracy matters for your equipment setup. The performance comparison table helps here. It shows which supplier fits your production demands.
Ready to upgrade your filtration system? Request technical datasheets from 2-3 manufacturers you like. Most provide free samples. They also offer pilot testing programs. You can test performance before placing bulk orders. One filter change could transform your casting quality.
What’s your biggest filtration challenge? The right partner from this list can solve it.