Wonder how factories keep their air clean for health and safety rules? HEPA and ULPA filters do the heavy lifting. They trap over 99.97% of tiny particles that regular filters miss.
You’ll find them in pharma cleanrooms and chip-making plants. Pick the wrong filter type? You could waste thousands on energy bills and still fail safety checks.
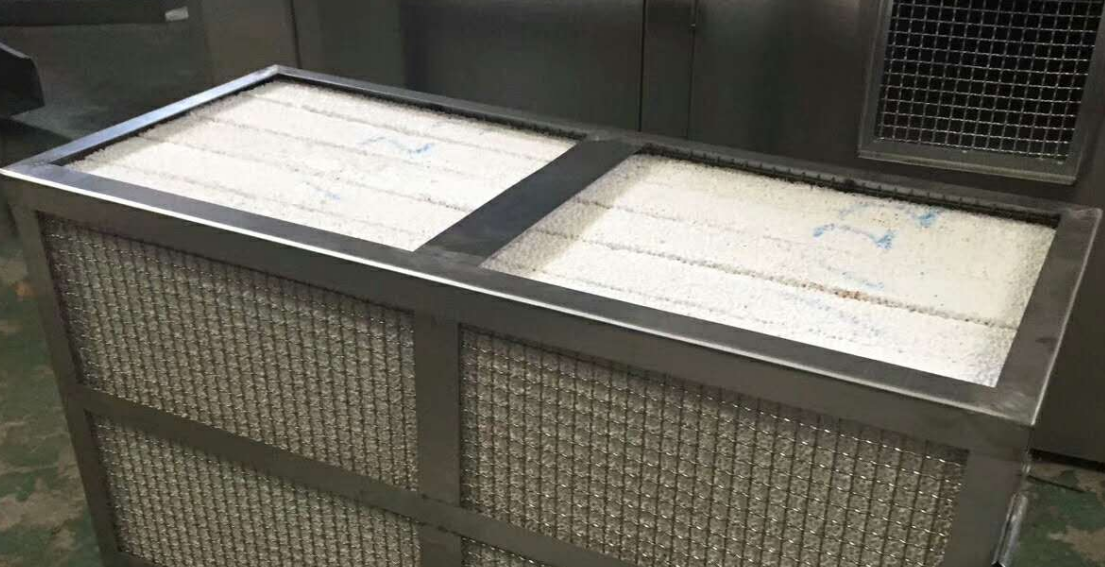
HEPA and ULPA Filters
HEPA (High-Efficiency Particulate Air) filters catch at least 99.97% of airborne particles at 0.3 micrometers. This
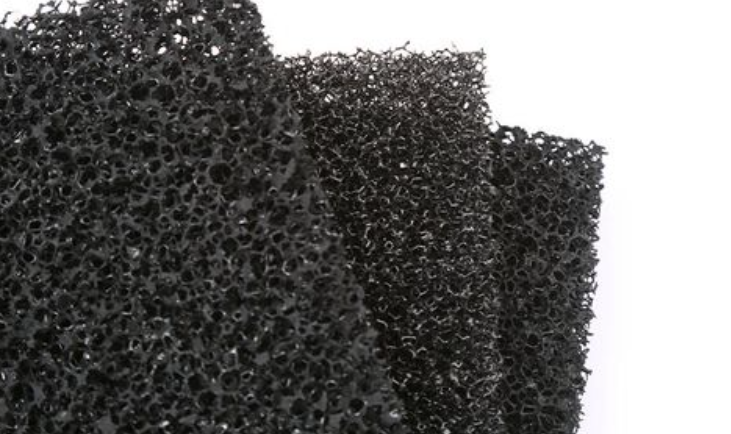
Activated Carbon Filters
Activated Carbon filters are key for cleaning air and water in factories. They trap contaminants really well. These filters remove oil vapors, VOCs, hydrocarbons, odors, chemicals, and some toxic stuff from gases and liquids.
Filter Media and Performance
High Surface Area: The carbon media has internal surface areas between 500 and 1500 m²/g. This catches more contaminants.
Media Types: Factories use three main types. Granular activated carbon (0.5–4 mm), powdered carbon (1–150 μm), and extruded carbon (0.8–4 mm). Pick the type based on what you need to remove.
Performance Figures:
-
Oil vapor removal: Gets levels below 0.003 mg/m³ in compressed air systems.
-
Particle retention: Meets ISO 8573-1 retention class 2 with microfiber fleece stage.
-
Pressure drop: Built to keep pressure drops low, even with high flow. This saves energy.
-
Odor and color removal: Removes VOCs and organic odors. Works for air and water color removal too.
Typical Industrial Applications
-
Compressed air cleaning and instrument air systems
-
Food and beverage processing
-
Packaging and filling machinery
-
Sterile air pre-filtration
-
Factory water treatment (removes chlorine, tastes, odors)
-
HVAC odor control in offices and public buildings
Construction Designs and Industrial Brands
Donaldson AK Elements: Two-stage design with Activated carbon and microfiber fleece. Has reinforced sleeves. Carbon loading goes up to 650 gsm for pleated filters.
Atlas Copco ASC Cartridges: High-purity sintered carbon block with polypropylene pre-filter. Strong cage design stops channeling or bypass. Good for color-sensitive and heavy-duty jobs.
Operational Guidelines and Maintenance
-
Contact Time & Exchange Frequency: Filters last 1 month to 1 year. This depends on contact time needed and how much contamination you have.
-
Volume Limits: Big setups might hit transport limits for used carbon. Some grades max out at 3 m³.
-
Maintenance: Put pre-filters before the activated carbon. This protects it and makes it last longer.
Standards and Compliance
These filters meet ISO 9001, EU 1935/2004, FDA Title 21, and USP Class VI. You get material safety and full tracking.
Specialty Features and Panel Designs
-
Carbon Loading: HVAC filters range from 200 gsm to 650 gsm. Blends up to 600 gsm use a 50/50 carbon mix.
-
Panel Construction: Carbon ‘biscuits’ sit in metal frames. Easy to maintain. You can scale up with front or side-withdrawal housings.
Example of Use
Take a commercial compressed air system with a multi-stage filter. It has an activated carbon element. This setup hits ISO8573-1 class 2 particle retention. Oil vapor stays below 0.003 mg/m³. It supports food and beverage processing gear for over a year. Pressure drops stay under 100 Pa for best energy use.
Effectiveness and Industry Selection Tips
VOC and Vapor Removal: Standard filters cut VOCs and oil vapors by over 99%. ISO and European standards verify this.
Selection Criteria: Look at required flow, contamination level, filter life, energy use, and rules compliance. These factors matter most.
Baghouse Filters
Baghouse filters control dust and particles in heavy-duty industrial settings. You’ll find them in cement plants, steel mills, power stations, woodworking shops, and food or pharmaceutical plants. These units use fabric bags grouped together. Air flows through the bags. Dust gets trapped. Clean air comes out.
Performance and Capacity
-
Airflow Range: From 600 to over 2,500,000 CFM. This covers small shops to major power plants.
-
Filter Area: Units range between 598 and 5,600+ sq. ft. of filtering surface. Size and bag count determine this.
-
Bag Dimensions: Bags are 36–120 inches long and 4–8 inches in diameter.
-
Dust Storage: Models store 33.5 to 240 cubic feet of dust. Total unit weights can reach up to 13,000 lbs.
Types of Baghouse Filters
Pulse-jet baghouse: This is the most common type. It has automated cleaning. You get large airflow capacity and longer filter bags.
Shaker and reverse-air models: These offer semi-automatic or manual cleaning. Perfect for mid-sized operations or lower dust loads.
Filter Media and Selection
-
Polyester felt: Budget choice for general dust.
-
Nomex (aramid) felt: Works at high temperatures. Resists up to 450°F.
-
Fiberglass: Handles extreme heat and harsh environments.
-
PTFE membrane: Great chemical resistance. Captures very fine particles.
Pick the right bag material based on your dust type, operating temperature, and industry needs.
Operational Details
-
Efficient Cleaning: Air pulses or mechanical shaking remove dust. It drops into a hopper for safe disposal.
-
Air-to-Cloth Ratio: Best performance happens at 1–4 ft³/(ft²·min).
-
High Collection Efficiency: Over 99% of particles larger than 1 micron get captured. This meets strict OSHA and ISO emission standards.
Industrial Applications
-
Cement: Controls clinker dust.
-
Steel manufacturing: Removes smoke and fume particles.
-
Power plants: Captures ash from combustion gases.
-
Wood and metalworking: Collects sawdust and fine metal dust.
-
Pharma/food: Keeps air sterile. Ensures product safety.
Advantages and Considerations
Stable, reliable performance for large and fine particles.
Withstands sticky, water-attracting, or hot dust.
Key factors to consider: Particle size, needed airflow, rules compliance (ISO, OSHA), and pressure drop for energy savings and bag life.
The right cleaning system and filter material give you effective dust control. You get lower maintenance. Your bags last longer, even in the toughest industries.
Cartridge Filters
Cartridge filters rank as a top pick for industrial air systems. They deliver strong filtration, take up less space, and work across many sectors. You’ll find them in dust collection, process ventilation, and HVAC.
Key Features and Performance Data
MERV Ratings: industrial cartridge filters range from MERV 10 to MERV 16. The higher-end filters (MERV 16) perform close to HEPA-grade. They catch very fine particles, even submicron ones. This makes them great for welding fume extraction and pharmaceutical manufacturing.
Filtration Efficiency: Most cartridge filters hit over 98% efficiency at 10 microns. advanced nanofiber options can reach up to 99.97% at 0.3 microns. This gives near-perfect filtration for critical spaces.
Micron Ratings: You can get 1–10 micron ratings for standard and high-purity needs. 1 µm or lower works for microelectronics and pharma. 5–10 µm handles general industrial use.
Construction and Design Innovations
Pleated Media: The pleated design boosts the surface area for dust collection. This extends filter life and cuts pressure drop. Plus, it keeps airflow stable and lets dust release fast during cleaning.
Media Choices:
-
80/20 cellulose-polyester blends (industry standard)
-
Synthetic media with nanofiber overlays for ultrafine particle capture
-
Fire-retardant types for hazardous areas
-
Specialty coatings for moisture, oil, static, or chemical resistance
End Cap Designs: You get both double open end (DOE) and single open end (SOE). Materials include galvanized steel, PVC, and stainless steel. These boost durability and resist chemicals.
Structure: Cages and frames use galvanized or stainless steel for strength. Sealants and gaskets prevent leaks, even under high flow.
Physical Specifications and Compatibility
Sizes: Most range from 10 to 40 inches in length and 8 to 13 inches in diameter. Weights span 3–7 lbs.
OEM Fit: These filters replace original parts in systems from Donaldson, Robovent, Trion, and Micro Air.
Configurations: Made for both top-load and bottom-load collector setups.
Industrial Applications
Dust Collection: Factories, metal shops, food and pharma processing, and precision industries use these. They catch dust, powders, and fine particles reliably.
Fume and Vapor Extraction: Flame-retardant and high MERV media work great here. They handle welding, soldering, and other processes that create hazardous submicron fumes.
Engine Intake and Compressed Air Systems: These filters protect sensitive equipment from abrasive particles. They keep air standards clean.
Typical Environments: OSHA- and ASHRAE-regulated sites need high airflow and strict particle control. These filters deliver.
Examples and Comparative Figures
Standard Cartridge Example: 12.2″ x 10.5″ x 10.5″, ~4 lbs., pleated synthetic media, 98% at 10 microns.
Performance: Nanofiber cartridges reach 99.97% at 0.3 microns. That matches the best HEPA filters. Use them where you need the cleanest air.
Selection, Customization, and Maintenance
Tailored Media and Pleats: Pick Filter Media and pleat count based on dust load, airflow needs, and your application. High pleat count delivers more airflow. Lower pleat count helps dust release easier.
Special Features: Choose coatings for antistatic, fire retardant, chemical, oil, and moisture resistance as needed.
Easy Replacement: These filters install without tools. Quick swap-outs mean fast maintenance and less downtime.
Filter Life: Built for long service in dusty and heavy-load spaces. Just size and maintain them right.
Electrostatic Precipitators (ESPs)
ESPs offer top-tier air cleaning for industrial use. They remove particulate matter, mist, smoke, and fumes at 95% to 99% efficiency. You get great results with ultrafine particles as small as 0.01 microns. Facilities needing strict air quality control rely on this technology.
Performance and Energy Efficiency
High removal efficiency: Captures 95%–99% of mist, smoke, and tiny particles. Standard filters miss these.
Ultrafine particle capture: Removes particles down to 0.01 microns. This matches HEPA filter results. Performance stays strong at air speeds up to 2000 feet per minute.
Low pressure drop: ESPs run with less than 0.2″ pressure drop. This cuts fan and energy needs.
Energy savings: Facilities cut air cleaning and makeup air costs by up to 80% versus traditional filters.
Key Features and Technical Details
Reusable collector plates: Made from carbon steel (0.05 to 0.2 cm thick) or stainless steel for harsh settings. You can wash these plates. This removes ongoing filter replacement costs.
Advanced particle charging: Uses field charging and diffusion charging. This boosts capture rates for many particle types.
Electrostatic operation: Discharge electrodes and grounded plates create an electric field. Particles stick as air flows through. Cleaning happens by washing or shaking the plates.
Wet ESP options: Some models use water-washed collectors. Water flushes away dust all the time. This stops particles from getting back into the air and keeps things cleaner.
Real-time monitoring: Modern ESPs include optical particle counters. These track how well filtration works and meet clean air rules.
Applications and Industrial Examples
Industry uses: ESPs work in metalworking shops, plastics plants, food facilities, and hospital HVAC systems. They scale from small shops to large centralized sites.
Resource reclamation: Units catch and recover cutting oils, lubricants, coolants, and plasticizers from air streams. This cuts material loss and environmental waste.
Notable models:
-
UAS Smog-Hog: Hits 95% efficiency in tough compliance settings.
-
Purified Air ESPi 600/1000: Delivers up to 99% efficiency in compact and large setups.
-
Soft X-ray Enhanced ESP: Gets HEPA-level results at higher air flows. Operating costs stay low—perfect for hospitals and cleanrooms.
Advantages and Limitations
Advantages:
-
Airflow stays steady without clogging. No disposable filter waste.
-
Energy and maintenance costs drop over time.
-
Real-time tracking and documentation meet regulatory needs.
-
Quiet operation with low upkeep. Washable and reusable parts make this possible.
Limitations:
-
Installation costs more upfront.
-
Electrodes and plates need regular cleaning to stay efficient long-term.
-
Won’t work against gases or VOCs unless paired with other filtration tech.
Technical Highlights
-
Pressure drop: Less than 0.2″. That’s about 10 times lower than traditional HEPA filters. Energy efficiency stays excellent.
-
Performance at velocity: Keeps over 95% particle collection even at high airflow rates. Many fabric or cartridge filters lose efficiency under these conditions.
ESPs stand out as one of the most efficient, energy-saving air filtration choices for industrial sites. High particle levels and ultrafine particles create serious air quality problems. ESPs handle these challenges well.
How to Choose the Best Industrial Air Filter
Pick the right industrial air filter by focusing on these key factors. You get top filtration and stay compliant.
Identify Contaminant Type and Particle Size
Contaminant Type: Figure out your main problem. Is it dust, fumes, VOCs, oil vapors, chemicals, or germs? Welding shops need high-efficiency filters to catch metal fumes. Solvent facilities need activated carbon filters to remove VOCs.
Particle Size: Match your filter to the particle size you need to capture. HEPA filters remove particles as small as 0.3 microns. Pharma and electronics industries rely on them. Woodworking creates larger particles. Bag filters handle these well.
Airflow and Performance Metrics
Airflow Capacity: Pick filters that handle your facility’s airflow without creating high pressure drop. V-bank filters work great for large systems and turbulent air. They also cut energy use.
Efficiency and MERV Ratings: Most industrial sites need MERV 10 or higher. MERV 13 filters capture 90% of particles in the 1–3 micron range.
Operating Environment and Durability
Environmental Conditions: Think about temperature, humidity, and chemical exposure. Stainless steel or aluminum filters last longer. They resist corrosion in tough conditions.
Physical Nature of Pollutants: Check if pollutants are dry, moist, combustible, or explosive. Then pick your filter media and build to match.
Compliance and Standards
Regulatory Requirements: Your filters must meet ISO, OSHA, EPA, and industry standards. OSHA’s Permissible Exposure Limits (PELs) set minimum filter efficiency for hazardous dusts.
Certifications: Look for filters tested by ASHRAE, ISO, or OSHA. This confirms their filtration efficiency.
Filter Media and Types
Media Selection: You’ve got options. synthetic fibers work for durable, medium-efficiency bag filters. Cellulose is another choice. Activated carbon handles VOCs and chemical vapor.
Common Filter Types:
-
Cardboard frame pleated filters: Basic dust removal.
-
V-bank filters: High dust load and airflow.
-
All-aluminum/stainless steel: High durability.
-
Medium efficiency bag filters: Strong performance with synthetic fiber media.
Maintenance, Cost, and Service Life
Maintenance and Lifespan: Filters range from disposable to reusable. Reusable units cost more at first. But high-usage sites save money because they last longer and need fewer replacements.
Operating Costs: Compare upfront filter cost against lifetime costs. Factor in energy use and maintenance. High-efficiency filters often cut system energy use over time.
Application Examples and Installation
Application Cases:
-
Automotive bodywork needs filters for solid particles.
-
Chemical plants use carbon filters to remove hazardous gases.
-
Gas turbine intakes in power plants need tough, high-flow V-bank filters.
Space and Compatibility: Check that the filter fits your existing systems. Make sure you have space for installation and maintenance.