Reticulated foam filters work across dozens of industries. You’ll find them in medical clean rooms, industrial air systems, automotive engineering, and even aquarium maintenance.
These open-cell polyurethane structures stand apart from traditional filtration media. They combine high porosity with mechanical strength. Plus, you can customize their filtration efficiency. Conventional filters can’t handle certain challenges. These foam filters solve those problems.
Are you an engineer specifying components for a critical application? Maybe you’re a product designer exploring lightweight filtration solutions. Or perhaps you’re a procurement professional evaluating cost-effective alternatives. Reticulated foam filters have distinctive properties and diverse capabilities. Understanding them opens up solutions you might have missed.
This guide covers their molecular structure and chemical resistance. You’ll see real-world applications across eleven major industries. We also break down the essential criteria for selecting the right foam filter for your specific needs.
What Is Reticulated Foam Filter
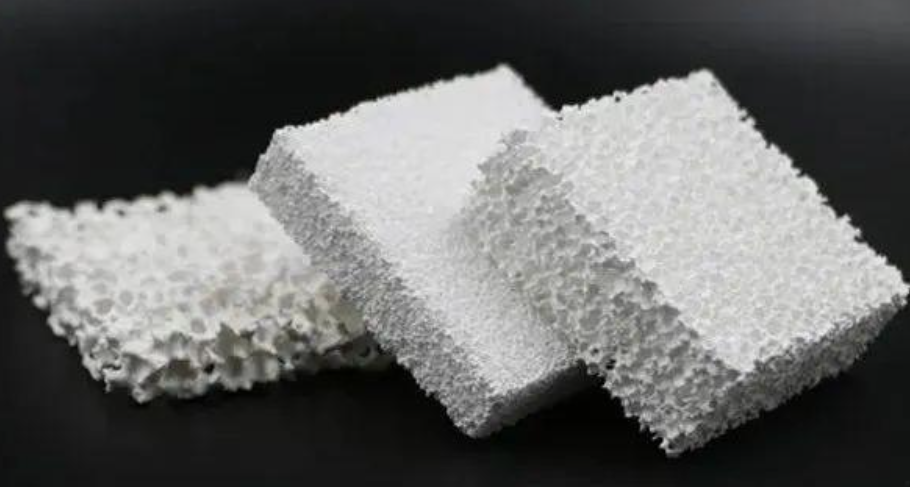
A reticulated foam filter is polyurethane foam that goes through a special reticulation process. Technicians remove the internal cell walls during production. This leaves a three-dimensional skeletal network structure.
The result? About 97% void volume throughout the material.
Traditional filters trap particles on their surface. Reticulated foam filters work another way. They capture contaminants within the cell structure itself. This depth-loading mechanism spreads particles throughout the foam thickness. You get longer service life. Plus, you get higher dirt-holding capacity.
Material Chemistry Options
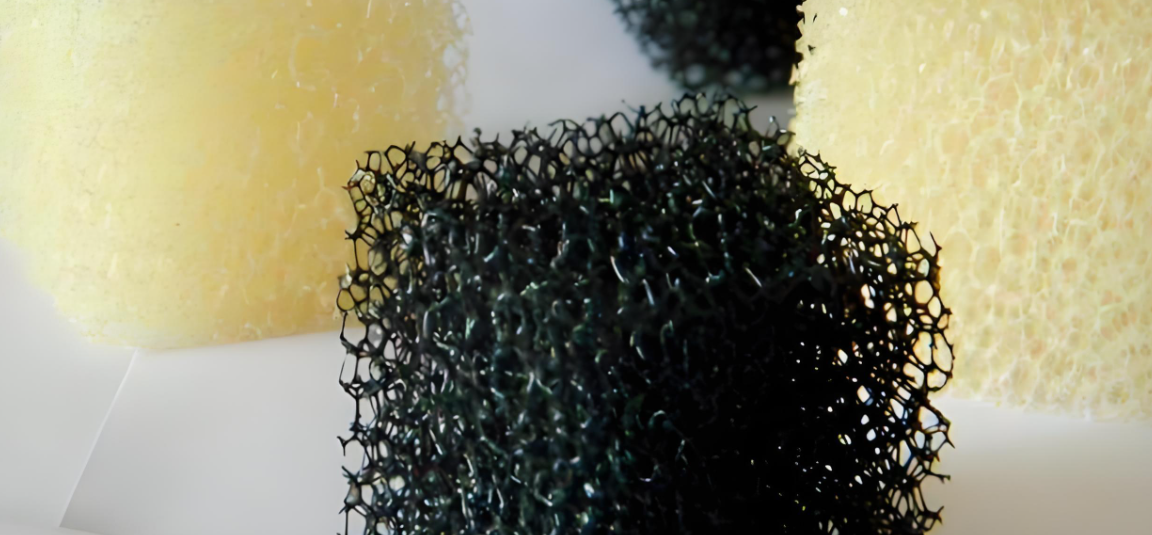
Manufacturers make these filters from two main polyurethane types:
Polyester polyurethane delivers superior mechanical strength. It handles higher temperatures better than other options. Engineers pick this type for demanding industrial uses.
Polyether polyurethane resists hydrolysis well. It performs well in humid environments and wet conditions. Water resistance and oil resistance make it ideal for liquid filtration tasks.
Both types can be compressed during production. This creates felted filter media with better dust-holding properties.
Pore Density Specifications
PPI (pores per inch) determines filtration performance. Standard reticulated foam filters range from 3 to 110 PPI. Industrial air and liquid applications use 10 to 60 PPI grades most often.
Common polyester foam specifications include:
– Grade 3015: 13–23 PPI
– Grade 3020: 15–25 PPI
– Grade 3030: 25–35 PPI
– Grade 2545: 45 PPI
– Grade 3060: 60 PPI
– Grade 3080: 80 PPI
Higher PPI numbers mean finer filtration. Lower PPI allows greater airflow with less pressure drop.
Key Structural Properties of Reticulated Foam Filters
The skeletal network inside reticulated foam filters creates performance that traditional filters can’t match. Each structural feature affects how these filters capture particles and manage airflow.
Void Volume and Open-Cell Architecture
Reticulated foam filters maintain 97% void volume throughout their structure. The open windows in each foam cell occupy 95-98% of the total mass and volume.
Cells form dodecahedron shapes. Manufacturing removes the internal walls. This leaves skeletal struts behind. Every cell connects to its neighbors. You get an open, three-dimensional network.
This connected structure explains why these filters resist clogging. Particles spread throughout the depth. They don’t pile up on the surface.
Pore Structure and PPI Control
Manufacturers control cell uniformity through PPI specs. Reticulated foam filters range from 4 to 100 PPI. Filter applications use 10-90 PPI grades.
Standard PPI options include 10, 20, 30, 45, 60, 80, and 100. Tech data sheets list specific choices like 20, 35, or 60 PPI for particular uses.
Bulk Density Specifications
These foam filters weigh between 1.4 and 2.1 lb/ft³ (22-34 kg/m³). Density varies by PPI rating and polymer type.
A 20 PPI foam measures 1.4 ± 0.10 lb/ft³. FilterPore™ E series at 10 PPI ranges from 1.4 to 1.6 lb/ft³. Flame-retardant polyester grades at 10 PPI reach 1.7-2.1 lb/ft³. Polyether variants measure around 27 kg/m³ for 20, 35, and 60 PPI grades.
Mechanical Strength Characteristics
Reticulated foam filters combine flexibility with durability. Tensile strength ranges from 50 to 270 psi depending on the grade. Elongation reaches 200-350%. Tear strength measures 5-35 lb/in.
Polyester reticulated foams at 10 PPI deliver tensile strength above 12 psi. Elongation exceeds 70%. Flame-retardant variants achieve 14 psi tensile strength with 150% elongation.
Compression performance matters for filtration stability. A 20 PPI filter shows minimum 10 lb/in tensile strength. Compression set at 50% stays below 15%.
Compressed felt variants reach firmness values up to 20. Manufacturers can compress 90 PPI base foam down to 0.025 inches (0.64 mm) final thickness. Higher compression increases flow resistance. Compressed grades work well for capturing finer particles.
Chemical and Environmental Resistance
Polyurethane chemistry decides if reticulated foam filters can handle tough conditions. The polymer core fights off most industrial chemicals. It stays stable across wide temperature swings.
Chemical Compatibility Profile
Polyester-based reticulated foam filters stand up to acids, bases, and organic solvents. Petroleum products won’t break them down. Industrial cleaners can’t destroy the skeletal structure.
Polyether types shine in water-based settings. They fight off hydrolysis during long periods of continuous water exposure. Unlike standard foams that might rot or lose integrity when wet, polyether variants keep their structure. This makes them the smart choice for aquarium filtration, outdoor ponds, and industrial wastewater systems where moisture is constant.
Filtration Performance Benefits
Reticulated foam filters beat standard filters in three key ways: particle capture, energy use, and how long they last.
Superior Particle Capture Across Size Ranges
The 3D skeleton structure traps particles deep inside. Surface filters can’t do this. Tests show these filters match MERV 8-13 ratings while maintaining significantly lower airflow resistance than pleated paper filters. Because the entire thickness of the foam catches dirt—not just the top layer—the filter doesn’t clog as quickly. This “depth loading” means you get steady airflow for longer periods before needing a replacement.
Environmental Operating Conditions
Chemical exposure demands documented resistance data. Acids, bases, and organic solvents attack specific polymer types. Polyester and polyether grades provide proven resistance. Review compatibility charts before picking the final material specification. Guesswork here is dangerous; choosing the wrong foam for a corrosive environment can cause the filter to swell and block flow, or even dissolve and contaminate the very system it was meant to protect.
Air and Gas Filtration Applications
The gas-phase filtration market will grow from USD 2.21 billion in 2025 to USD 2.75 billion by 2029. That’s a 5.6% CAGR over four years. North America leads this expansion. The regional industrial air filtration market hit USD 8,456.7 million in 2024. It jumps to USD 8,871.1 million in 2025 and reaches USD 14,313.1 million by 2035.
Reticulated foam filters grab their biggest market share in two places: semiconductor cleanrooms and chemical processing plants. Chip makers need filters that catch gas at the molecular level. One dirty particle can ruin entire wafer batches. Semiconductor sales hit USD 574 billion in 2022. This boom creates more need for top-grade gas filtration systems.
Chemical and petrochemical plants use these filters in a different way. The filters catch corrosive gases before they harm equipment. Power plants put them before turbines and compressors. Data centers use them to shield server racks from airborne molecular pollution. Hospitals install them in operating rooms and drug production zones.
U.S. air pollution drains over USD 131 billion each year from the economy. This comes from healthcare costs and lost work hours. WHO data shows 3.68 million early deaths each year in poorer countries from outdoor air pollution. These numbers make regulators push harder. The Clean Air Act and EPA emission rules make manufacturers upgrade their filtration systems.
The U.S. air filter market alone grows from USD 4.33 billion in 2024 to USD 7.44 billion by 2032. That’s a 7.1% CAGR. Industrial segments grow even faster. Air filtration systems take 38.5% of the industrial filtration market. They’re set to grow at 7.4% CAGR through 2034.
Metals and mining sites face the toughest OSHA workplace air rules. Auto plants need cleaner air for paint booth work. Drug makers must hit FDA cleanroom standards. Each industry finds new ways to use reticulated foam filters.
Liquid and Fluid Filtration Applications
U.S. municipal water treatment plants processed 34 billion gallons each day in 2024. Industrial facilities added another 18 billion gallons. Reticulated foam filters handle more of this volume than ever before. The open-cell structure catches suspended solids. Traditional media gets clogged by these same particles.
The global liquid filtration market jumped from USD 3.2 billion in 2024 to USD 5.0 billion in 2025. Projections show USD 10.7 billion by 2035. That’s a 7.9% compound annual growth rate. Municipal treatment takes 44% of this market. Industrial applications grab the remaining 56%.
Regional Industrial Applications
North America dominates with 40% of global revenue. The region’s industrial filtration sector grew from USD 16.83 billion in 2023. It’s projected to reach USD 21.50 billion by 2030. Gulf Coast chemical plants install reticulated foam filters in process streams. Midwest manufacturing facilities use them for coolant filtration. Northeast pharmaceutical companies put them in sterile water systems. Western food processors use them for beverage clarification.
Asia-Pacific captures 39.85% of the market. India leads regional growth at 9.1% CAGR through 2035. Gujarat’s chemical corridor uses these filters for solvent recovery. Tamil Nadu textile mills filter dye baths. Maharashtra pharmaceutical plants meet zero-liquid-discharge mandates. They use multi-stage foam filtration systems.
Performance Advantages
Reticulated foam filters remove 70-80% of contaminants. Standard settling methods can’t match this performance. The three-dimensional network traps particles throughout the foam depth. Engineers combine these filters with membrane, depth, and cartridge systems. Particle size affects the selection. Flow rate matters too. Required efficiency determines the final choice.
Polymer-based variants dominate 36.24% of material choices. Cotton and aramid blends work in tough spots. High-temperature environments need these materials. So do areas with harsh chemicals.
Acoustic and Noise Control Applications
Reticulated foam filters absorb sound waves. Their connected cell structure does the work. The foam’s skeleton network turns sound energy into heat. Sound waves bounce between foam struts. This friction cuts noise across many frequency ranges.
The noise control system market hits USD 10.8 billion by 2035. Growth runs at 4.8% each year from 2025 to 2035. Acoustic panels take 23% of the global market in 2025. They grow at 4.3% CAGR through 2035.
Building and Construction Integration
Commercial buildings account for 37% of total acoustic panel demand. This segment grows at 5.1% CAGR through 2035. The broader acoustic panel market jumps from USD 13.1 billion in 2024 to USD 21.5 billion by the forecast period’s end. It’s not just about sound panels, though. Reticulated foam is increasingly used to line HVAC ducts because it dampens reliable mechanical noise without choking off airflow—a balance that’s hard to achieve with denser materials.
Medical and Healthcare Applications
U.S. hospitals and clinics spend $63 billion yearly on healthcare IT. Reticulated foam filters protect critical equipment in this infrastructure. They clean operating room air supplies and shield sensitive cooling fans in diagnostic machines. Think about life-support devices like ventilators; they need consistent, pure airflow. These filters trap contaminants without creating dangerous pressure drops. Plus, they hold up well against the harsh sterilization chemicals typical in hospital settings, making them a trusted choice for patient safety.
Cushioning and Outdoor Furniture Applications
Outdoor furniture makers shipped $9.4 billion worth of cushioned products in 2023. Reticulated foam filters offer clear benefits for this market. The open-cell design stops moisture from building up. Standard closed-cell foams trap water. Mildew grows fast in those foams. The skeletal network in reticulated foam drains quickly. It stays dry.
The global outdoor cushions market jumps from USD 5.7 billion in 2023 to USD 9.4 billion by 2033. That’s 5.2% growth each year. North America accounts for USD 904.60 million in 2024. The region grows at 6.8% CAGR through 2031. U.S. sales alone climb from USD 446.70 million in 2024 to USD 616.47 million by 2032.
Material Performance and Weather Resistance
Reticulated foam filters paired with solution-dyed fabrics make outdoor cushions last longer. Premium acrylic covers like Sunbrella run USD 18-25 per yard. They last 10+ years with proper care. Solution-dyed polyester costs 40-50% less at USD 15-20 per yard. Colors stay vibrant for 5-7 years outdoors.
Foam density matters most for cushion selection. Quick-drying foam grades don’t hold moisture. Mildew can’t grow without moisture. Polyurethane foam costs jumped over 40% since October 2020. Polyethylene foam rose more than 20%. These price hikes push makers to try reticulated options. The high void volume cuts material costs. You still get strong performance.
Outdoor seat cushions alone reach USD 500 million in 2025. They hit USD 900 million by 2033. Olefin fiber ratings score 9/10 for stain and mildew resistance. PVC-coated polyester rates 8.5/10 for hot, humid climates. Reticulated foam filters inside these covers drain better than solid foam cores.
Selection Criteria: Choosing the Right Reticulated Foam Filter
Four key factors decide if a reticulated foam filter works for your setup. PPI rating controls particle size capture. Material chemistry affects chemical resistance. Operating environment sets temperature and humidity limits. Thickness balances flow rate against filtration efficiency.
PPI Rating and Porosity Selection
PPI (pores per inch) ranges from 4 to 100 in reticulated polyurethane foams. This number controls pore size and filtration performance.
Common pore sizes measure 0.5 to 5 mm. This equals about 4 to 80 PPI in standard filtration grades. Manufacturing tolerances run ±5 PPI from the nominal specification.
Lower PPI ratings (4-20) create very open structures. They handle heavy debris loads. Pressure drop stays minimal. Airflow remains high. These work well for prefiltration stages or coarse particle removal.
Mid-range grades (20-45 PPI) balance efficiency with flow capacity. HVAC systems use 20-30 PPI filters as standard. High-airflow compressors and blowers need 40-45 PPI ratings. A typical 20 PPI polyether foam weighs 1.5 lb/ft³.
High PPI options (80-100) trap fine particles well. The tight structure increases pressure drop. Flow rates decrease. These grades suit jobs where filtration efficiency beats throughput.
Thickness adds another variable. Thicker foam blocks more airflow at the same PPI. Thinner foam increases flow rate but reduces particle capture depth.
Material Chemistry: Polyester vs Polyether vs Polyurethane
Polyester reticulated foam delivers maximum mechanical strength. It resists solvents and chemicals better than alternatives. Engineers pick this type for top durability. High-stress industrial environments benefit from polyester’s structural stability.
Polyether reticulated foam feels softer and more flexible. It handles water exposure without breaking down. Water-friendly properties make it ideal for wet environments and high-humidity conditions. This material fights acids and bases well. A 20 PPI polyether grade at 1.5 lb/ft³ works in air filtration, water purification, and sound absorption. UV resistance makes it suitable for outdoor installations.
Standard polyurethane reticulated foam sits between these two options. It’s stronger than polyether but less robust than polyester. Temperature tolerance runs higher than polyether grades. Water absorption creates problems though. Moisture supports mildew growth. Don’t use generic polyurethane where filters stay wet.
Environmental Operating Conditions
Temperature extremes rule out certain foam types right away. Polyurethane-based filters tolerate higher operating temperatures. Match the foam’s temperature rating to your system’s peak values.
Water contact frequency changes material selection. Continuous immersion requires polyether or bacteriostatic-coated variants. Standard polyurethane absorbs water. Mildew colonies grow inside the foam structure. High-humidity environments need the same consideration.
UV exposure breaks down unprotected foams fast. Outdoor HVAC units face direct sunlight. Indirect UV still breaks down foam over time. PVC-coated reticulated foam filters solve this problem. The RET-20 polyether grade includes UV stabilizers for outdoor use.
Chemical exposure demands documented resistance data. Acids, bases, and organic solvents attack specific polymer types. Polyester and polyether grades provide proven resistance. Review compatibility charts before picking
Conclusion
Reticulated foam filters work well across many industries. Their open-cell structure gives you high porosity and adjustable pore sizes. You get better airflow, precise filtering, and longer life than traditional filter materials.
These filters protect sensitive medical equipment. They also improve sound comfort in buildings. Chemical resistance? Check. Washable? Yes. Design flexibility? They adapt to your exact needs.
Engineering an HVAC system? Developing medical devices? Designing industrial filtration equipment? Understanding reticulated foam filter properties, benefits and applications helps you choose wisely. You’ll optimize both performance and cost.
Match the pore size, material, and structure to your filtration needs. That’s the key.
Ready to specify the perfect reticulated foam filter for your application? Talk to filtration specialists. They’ll analyze your requirements and recommend custom solutions that boost efficiency and meet your industry’s strict standards. Your ideal filtration solution is within reach.