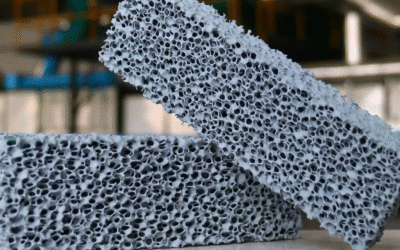
Choosing the right ceramic foam filter can make or break your foundry’s casting quality. Most Australian manufacturers find it hard to deal with international suppliers, conflicting tech specs, and compliance rules.
You might run a small aluminium workshop in Melbourne. Or you manage a large foundry in Perth. Either way, the gap between top filtration and poor performance comes down to one thing: knowing what to look for and where to get it.
This guide reviews Australia’s top ceramic foam filter suppliers—AdTech, Cangzhou Sefu, and FoundryMax. You’ll learn the key selection criteria, quality checks, and smart logistics options.
Here’s what you get: how to match filter materials (alumina, SiC, or zirconia) to your casting needs. Plus, you’ll decode the tech specs that truly count. You’ll also check if your supplier meets Australian standards. All this helps you source the best ceramic foam filters in Australia without the guesswork or expensive mistakes.
AdTech Ceramic Foam Filters – Non-Stick Aluminium CFF for Australia
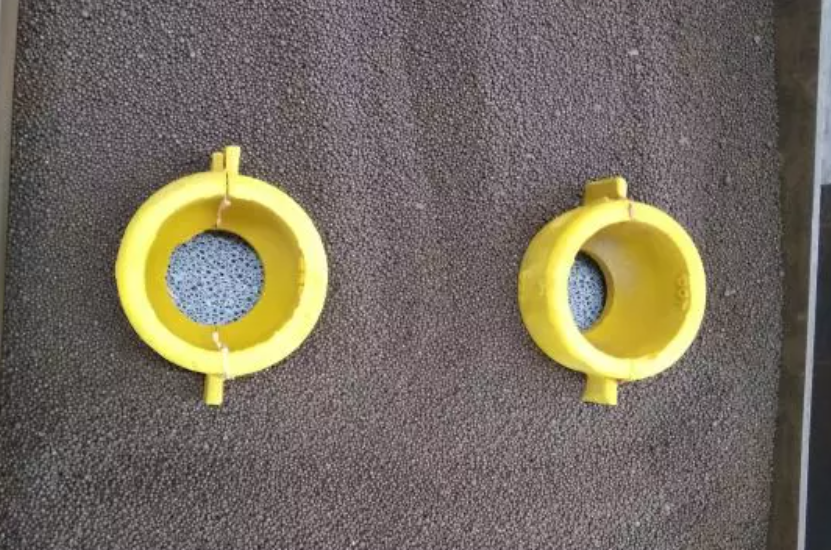
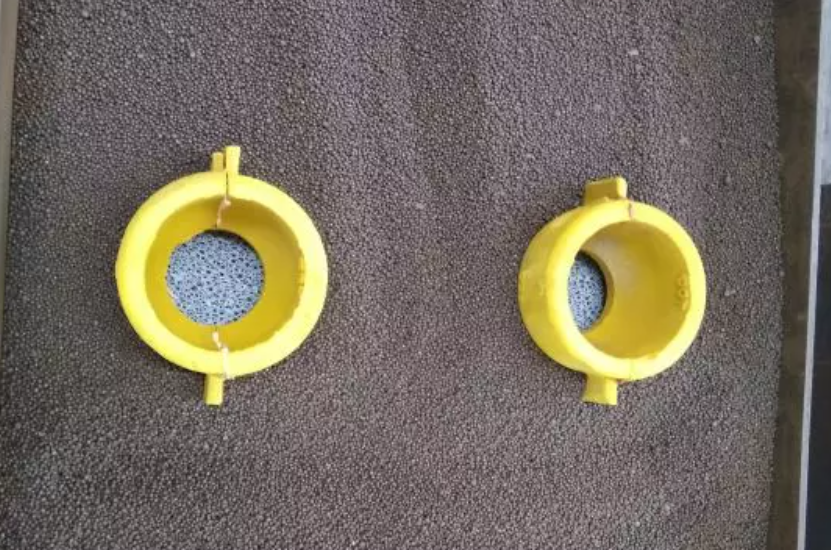
AdTech’s ceramic foam filters stand out in the Australian market. They use a proven three-dimensional network structure. Plus, they meet aviation-grade manufacturing standards. The company offers porosity options from 10 to 60 PPI. This gives you precise control over filtration performance. Match it to your specific melt flow needs.
Manufacturing Excellence That Meets Australian Standards
The production process uses 1180°C high-temperature sintering. This baking method cures the slurry coating onto the foam framework. The structure stays intact throughout the process. AdTech uses square center correction with automatic extrusion technology. This guarantees uniform material distribution across every filter. For aviation and transportation aluminum alloy precision castings, consistency impacts part reliability.
The three-dimensional network forms through connected organic bubble pores. You get uniform mesh patterns on both surface and cross-section. High porosity comes from a drainage manufacturing method. This maximizes flow capacity. Filtration efficiency stays high.
Non-Stick Surface Technology for Zero Contamination
AdTech’s non-stick coating solves a common foundry headache: secondary pollution from filter breakdown. Run your hand across the surface—it stays clean and dry. No sticky residue means no glue spray contamination entering your melt stream. This feature is essential for casting high-value components. Even trace impurities can harm mechanical properties.
The filters trap both micron-level and large oxidized inclusions. They stay stable throughout the pour. Ceramic particles won’t break off into your finished castings.
For semi-continuous casting operations in Australia, AdTech recommends pairing ceramic foam filters with fiberglass pre-filters. This combination maximizes filtration efficiency. It works based on your specific impurity content and desired casting quality.
Melt drop measurements start at 50mm at the beginning. They increase to 60-120mm by casting end as inclusions build up on the filter surface. These are normal performance indicators for high-throughput applications.
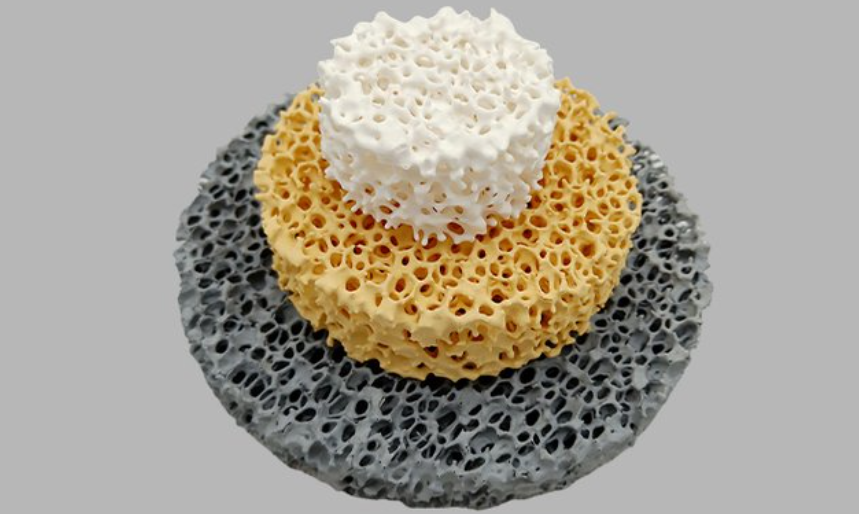
Cangzhou Sefu Ceramic – Multi-Material CFF Supplier (Alumina/SiC/Zirconia)
Cangzhou Sefu Ceramic New Materials Co., Ltd. has made ceramic foam filters for over ten years, serve the Australian market with ISO and SGS certification. They products ship from Tianjin and Shanghai ports.
What sets them apart? A complete multi-material CFF range. You get alumina, silicon carbide, and zirconia options from one supplier. No need to juggle multiple vendors for different metal types.
Material-Matched Solutions for Every Casting Metal
Alumina CFF works for aluminum and aluminum alloy filtration. The working temperature is 1100°C. Pore densities range from 10 to 40 PPI. Porosity runs 80-90% for maximum melt flow. Thickness options span 15-50mm to fit your gating system depth.
These filters survive 6 thermal shock cycles at 1100°C without cracking. Mechanical strength reaches 0.6 MPa bending strength and 0.8 MPa compression strength. Filtration efficiency hits 85% for aluminum melts.
Silicon Carbide (SiC) CFF fits cast iron and copper-based alloy foundries. These sic filters handle tough impurity loads in ferrous and copper melts. Gas defects drop. Final casting cleanliness improves. SiC has high heat transfer properties. This keeps metal temperature steady during filtration.
Zirconia CFF serves Australian steel foundries. It works with carbon steel, alloy steel, and stainless steel. Temperature resistance is extreme – it handles molten steel at 1600-1700°C service range. Few ceramic foam filter suppliers offer all three materials. Sefu gives you complete foundry coverage.
FoundryMax / Ceramic Foam Filter Aluminium Application
FoundryMax ceramic foam filters boost aluminium casting quality through smart pore designs. The product line covers 10 to 60 PPI options. Each grade removes different inclusion sizes from your melt.
PPI Selection Guide for Aluminium Foundries
Pick your filter grade based on the cleanliness you need:
-
PPI 20 catches inclusions ≥80 μm with 78% filtration—works great for general aluminium castings where cost is key
-
PPI 30 captures particles ≥40 μm at 85% efficiency—perfect for automotive parts and structural pieces
-
PPI 40 traps inclusions ≥20 μm with 88% removal—best choice for precision aluminium alloy castings in machines
-
PPI 50 stops particles ≥10 μm at 92% efficiency—aerospace-grade filtration for vital parts
-
PPI 60 removes inclusions ≥5 μm with 95% filtration—ultra-fine mesh for premium castings that need zero defects
Large particles stick to the filter’s top surface. Small inclusions get caught inside the 3D pore network. This two-way action keeps metal flowing smooth during the pour.
Material Performance Under Australian Foundry Conditions
FoundryMax alumina-based CFF combines Al₂O₃ and SiO₂. Operating temperature hits 1100-1200°C. That’s far above aluminium’s melting point. Porosity runs 80-90% for top flow rates. Low density of 0.4-0.5 g/cm³ means less thermal mass to preheat.
Compressive strength reaches ≥0.8-1.0 MPa at room temperature. Rupture modulus hits 5.5 MPa at 816°C. These filters handle 6 thermal shock cycles at 1100°C without breaking. This toughness pays off during back-to-back pours in busy Australian foundries.
The filters boost tensile strength, elongation, and impact resistance in your final castings. Surface finish gets better. Scrap rates fall because you get fewer defects and less rework. Metal flow stays stable with a starting head of 100-150mm. This drops to 75-100mm as the filter fills with trapped dirt.
How to Choose the Best Ceramic Foam Filter for Your Australian Foundry
Three factors determine your filter choice: the metal you’re pouring, the quality grade you need, and the flow rate your production demands. Get these wrong? You’ll face blocked filters, incomplete pours, or contaminated castings.
Match Filter Material to Your Metal Chemistry
Alumina (Al₂O₃) filters work for aluminium and aluminium alloys. They handle temperatures up to 1200°C—well above aluminium’s melting point. Molten aluminium stays stable with this material. You need 80-90% porosity for proper flow. Compression strength must hit ≥1.0 MPa to handle pour pressure.
Custom sizes like 20x20x2 inch work well for aluminium sheets and foils.
Silicon Carbide (SiC) filters handle cast iron—both ductile and grey grades. They work at 1500°C. The material contains 50-60% SiC and 20-30% Al₂O₃. Compression strength reaches ≥2.0 MPa for the tougher iron environment.
A 150x150x22mm SiC filter processes 450kg of ductile iron or 900kg of grey iron before you need a replacement. Smaller 30x50x22mm units (15cm² area) filter 60kg grey iron at 4kg/s flow rate.
Zirconia (ZrO₂) filters are essential for steel foundries. They survive extreme heat up to 1700°C. Use them for non-alloy steel, low-alloy steel, high-alloy steel, and stainless steel. No other material handles this heat range.
Size Your PPI According to Quality Requirements
Low PPI (10-20) suits high-volume operations with heavy impurity loads. You get faster flow instead of ultra-fine filtration. Pair large-mesh filters with glass fiber pre-filters for general-quality castings.
High PPI (30-60) gives you precision filtration for aviation-grade and critical components. The 3D network traps tiny inclusions that low PPI misses. Flow rates drop, but casting quality improves significantly.
Flow benchmarks for grey iron (SiC filters):
– Φ50x22mm: 4.5 kg/s
– Φ100x22mm: 17 kg/s
– 150x150x22mm: 54 kg/s
Pick your filter size based on actual melt speed and inclusion density in your operation.
Verify Critical Performance Specs Before Purchase
Check these benchmarks against supplier datasheets:
|
Material |
Porosity |
Work Temp (°C) |
Comp. Strength (MPa) |
Thermal Shock |
Density (g/cm³) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Alumina |
80-90% |
≤1200 |
≥1.0 |
800°C→RT, 5 cycles |
≤0.5 |
|
SiC |
80-90% |
≤1500 |
≥2.0 |
1200°C→RT, 6 cycles |
0.36-0.5 |
Quality Inspection Checklist Before Purchasing
Australian foundries lose thousands of dollars on bad filters that fail mid-pour. Check filters before purchase to catch problems before they hit your production floor. Here’s a proven checklist suppliers can’t fake.
Color Uniformity and Surface Contamination Test
Pull the filter from its packaging. Compare it against an approved reference sample. Color consistency shows manufacturing quality control. Measure with a colorimeter if you have one. Otherwise, use visual inspection under proper lighting.
Acceptable color deviation limits:
– Exposed surfaces: ΔE ≤ 1.0–1.5 (you can’t see this difference with the naked eye)
– Non-critical areas: ΔE ≤ 2.0–3.0 (confirm exact tolerance with your supplier contract)
Set up your inspection station properly. Use D65 standard daylight or white light at 600-1000 lux intensity. Position yourself 60-70 cm from the filter at a 45° viewing angle. A neutral gray or white background stops color distortion.
Reject filters showing these defects:
– Impurity spots, color streaks, contamination marks, or uneven coating
– Individual spots >0.5 mm diameter visible at 60-70 cm distance count as major defects
– Three or more visible spots mean you need to re-inspect the full batch or reject it right away
Zero-glue coating verification protects against secondary pollution. Run your bare fingertips across the filter surface. Quality units feel clean and dry. No sticky residue. Poor filters leave a tacky film on your skin.
Wipe test procedure: Press a clean white cotton cloth against the surface. Rub hard five times. The cloth should show no sticky marks, gloss changes, or powder buildup. Any adhesive transfer means contamination risk.
Mechanical Integrity Tap Test
This quick field test shows internal bonding strength and sintering quality. Use a 100-200g rubber or wooden mallet—never a metal hammer. Metal hammers can create false damage.
Tap nine points: four corners, four edge midpoints, and the center. Use consistent light force at each spot.
Pass criteria:
– Minimal dust-like particles (less than 0.1% of sample weight)
– Clear, uniform ringing sound at all test points
– Zero flaking or chipping larger than 5×5 mm
Fail indicators:
– Ceramic slag keeps shedding during tapping
– Dull or inconsistent sound (signals internal cracks or poor bonding)
– Sheet-like or chunky pieces breaking off
Document your results right away. Three or more tap points showing bad response? The entire batch needs thermal shock testing before you accept it. Never skip this step. Filters that fail mid-pour contaminate your entire melt and ruin the casting.
Australian Casting Requirements: Direct Application Guide
|
Casting Type |
Recommended Material |
PPI Range |
Size (mm, typical) |
Flow Rate (L/min) |
Strength Req. (MPa) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Al Alloy Auto Parts |
Alumina/Zirconia |
20-40 |
50×50×25 |
50-100 |
>300 |
|
Cast Iron Pipes |
SiC |
10-20 |
100×100×25 |
100-200 |
>400 |
|
Precision Aero Parts |
Zirconia |
40-60 |
30×30×15 |
20-50 |
>500 |
Automotive aluminum parts need 50-100 L/min flow capacity. This keeps production moving. 50×50×25mm filters fit most gating systems. No modification needed. Cast iron pipe foundries demand larger 100×100×25mm SiC filters. These process 100-200 L/min. That’s double the aluminum rate. Iron melts carry heavier slag loads. Aerospace components require PPI 40-60 zirconia filters. Yes, the 20-50 L/min flow restriction is slower. But surface defects aren’t acceptable on turbine blades. Ultra-fine filtration justifies the slower pour speed.
Check these specs against your current filter performance. You’re using PPI 20 alumina for precision engine blocks? Upgrading to PPI 40 zirconia will drop your scrap rate significantly. Yes, initial filter cost increases by 30-40%. But the results are worth it.
Pricing and Logistics for Australian Buyers
Import costs for ceramic foam filters into Australia depend on three main factors: supplier FOB pricing, sea freight charges to your port, and Australian import duties. Your total investment gets determined by the landed cost before the filters reach your foundry floor.
Understanding Australian Import Cost Structure
Every filter shipment faces the same cost breakdown. Start with the supplier’s FOB (Free On Board) price. That’s what you pay for the product loaded onto the vessel at Chinese ports like Tianjin or Shanghai. Add international shipping to Sydney, Melbourne, or Brisbane. Then calculate GST at 10% on your landed value (CIF price plus any duties).
Total landed cost formula:
– FOB price (supplier’s quoted rate per piece or per cubic meter)
– + Sea freight (varies by container size and route)
– + Import tariffs (0-5% for most industrial machinery under AHECC codes)
– + GST (10% applied to CIF value plus tariffs)
– = Your delivered cost before local transport to foundry
Most ceramic foam filter suppliers accept T/T (Telegraphic Transfer) payment terms. Typical splits run 30% deposit on order confirmation, 70% balance before shipment. Large orders may qualify for L/C (Letter of Credit) through major Australian banks.
Price Impact from Currency and Import Trends
The Australian dollar’s strength affects your purchasing power. Recent AUD appreciation versus USD has cut import costs for machinery and industrial materials by 2.6-3.4%. A stronger AUD means your filter budget stretches further.
Australia’s Import Price Index hit 134.20 points in Q3 2025 (down 0.4% from the previous quarter). General industrial machinery prices dropped 2.6% quarter-on-quarter. This trend benefits foundries sourcing filters and related equipment. The annual import spend reached A$526.8 billion. China supplied 20.5% of this, covering refined petroleum, cars, and machinery.
Capital goods import prices tracked 130.40 points (2011-2012 base) in March 2025. Historical movements show volatility: +3.3% in Q1 2025, +0.2% in Q4 2024, -1.4% in Q3 2024. Monitor these indexes for bulk purchases. Time your orders during downward price movements. This maximizes savings.
Freight Routes and Container Options
Sea freight from Chinese ports to Australian foundries runs through three main corridors:
– Tianjin/Shanghai → Sydney: 18-22 days transit
– Tianjin/Shanghai → Melbourne: 20-24 days transit
– Tianjin/Shanghai → Brisbane: 16-20 days transit
Container selection depends on order volume. A 20-foot container holds about 1,500-2,000 standard-size filters (50×50×22mm). Larger 40-foot containers accommodate 3,500-4,500 units of the same size. Suppliers often require minimum order quantities matching half or full container loads. This optimizes freight costs.
LCL (Less than Container Load) shipments work for smaller foundries testing new suppliers. Expect 20-30% higher per-unit freight costs versus full container shipping. Lead times extend by 3-5 days due to consolidation schedules at origin ports.
Duty and Compliance Costs
Australian customs classify ceramic foam filters under specific AHECC (Australian Harmonized Export Commodity Classification) codes. Most industrial filtration products fall into the 0-5% tariff band. Verify your exact HS code classification with your customs broker before you finalize supplier contracts.
GST calculation example (50×50×22mm alumina filter batch):
– FOB price: $2,000 USD (1,000 pieces @ $2.00 each)
– Sea freight: $800 USD (LCL to Melbourne)
– CIF value: $2,800 USD (≈ $4,200 AUD at 1.50 exchange rate)
– Import duty (assume 5%): $210 AUD
– Taxable value: $4,410 AUD
– GST (10%): $441 AUD
– Total landed cost: $4,851 AUD before local delivery
Factor these costs into your per-piece pricing. The example above shows $4.85 AUD landed cost per filter before warehouse storage or domestic freight to your foundry.
Negotiating Better Terms with Suppliers
Large foundries placing repeat orders gain leverage. Request volume discount tiers during supplier qualification. Common breakpoints:
– 500-1,000 pieces: 5-8% off FOB price
– 1,001-3,000 pieces: 10-15% discount
– 3,001+ pieces: 15-20% reduction (negotiate custom pricing)
Payment flexibility improves with order history. After 3-5 successful shipments, suppliers may accept 60-day payment terms. They might reduce deposit requirements to 20%. Build relationships with your logistics provider. Consolidated shipping across multiple product lines cuts per-container costs by 10-15%.
Import volume data shows goods imports up 1.4% quarter-on-quarter in Q3 2025. This includes refined fuels and industrial materials. Australian foundries benefit from established trade channels with Chinese manufacturers. The Australia-US Free Trade Agreement (AUSFTA) generated +30% import/export revenue gains in relevant sectors. This proves that smart sourcing reduces long-term costs.
Track the Import Price Index each month through the Australian Bureau of Statistics. Plan bulk filter purchases during downward price cycles. Combine orders with other foundry supplies. This maximizes container use and minimizes freight waste.
Conclusion
Picking the best ceramic foam filters in Australia boils down to three key factors: does the material fit your casting process, can you trust the supplier, and do they meet certification standards?
You’re filtering aluminium with AdTech’s non-stick tech? Good. Handling high-heat alloys with Cangzhou Sefu’s multi-material options? Smart. Boosting foundry efficiency with FoundryMax? Even better. The right filter shapes your casting quality and cuts operational costs.
Don’t trade quality for a lower ceramic foam filter price. Compare technical specs and use the inspection checklist above to check suppliers carefully. Verify ISO certifications. Request test samples. Confirm Australian shipping details before placing bulk orders.
Ready to upgrade your filtration system? Reach out to your shortlisted suppliers with your foundry’s specific technical needs. Get custom quotes that cover shipping to your Australian location. Ask for performance data that matches your exact casting conditions. Premium ceramic foam filters cost more upfront. But they cut rejection rates and boost casting integrity over time.
Your perfect filter is out there. Now you’ve got the map to find it.