Picking the right reticulated foam filter gets tricky. You face dozens of technical specs and material choices.
Maybe you filter molten metal in a foundry. Or you keep aquarium water crystal-clear. Or you design specialized industrial filtration systems. You need to know the different types of Reticulated foam filters. This knowledge helps you get the best performance and longest life.
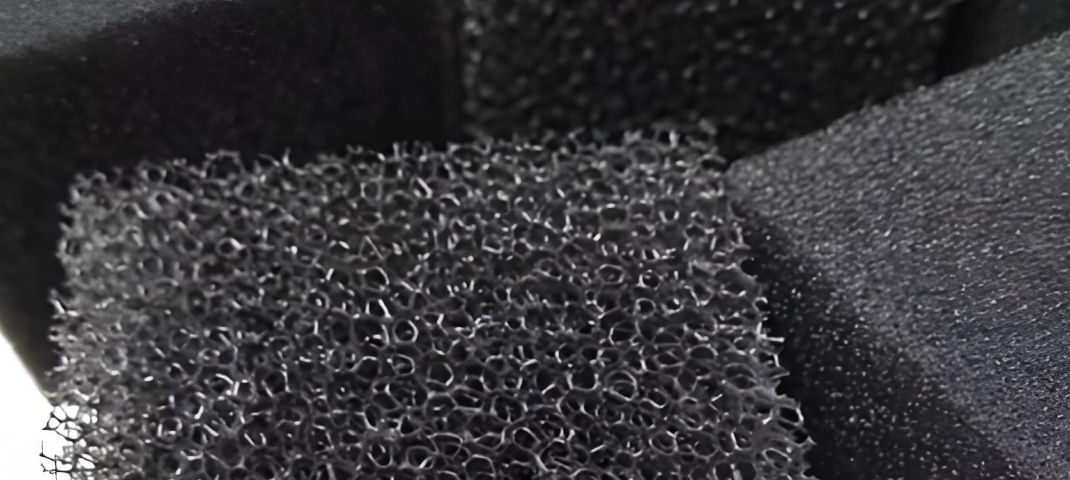
These open-cell foam structures don’t work the same for every job. They differ in chemical makeup, pore density, treatment coatings, and engineering for specific uses.
Look at Polyester versus polyether bases – that’s the basic split. Then check PPI ratings. Fire resistance matters too. So do specialty coatings. Each type does different jobs and performs differently.
Polyester vs Polyether Reticulated Foam Filters
Your filter’s chemical base controls how long it lasts and where it works best. Two materials lead the market: polyester (ester-based) and polyether (ether-based). Each one has different structure and performance.
Core Structural Differences
Polyester reticulated foam has a rigid 3D skeleton with even pore layout. The cell structure keeps many “windows” or closed cells that reflect light and limit airflow a bit. Pore sizes range from 0.5mm to 5mm, or 4 to 80 PPI. This tight, even pore spacing makes polyester perfect for fine filtering jobs.
Polyether reticulated foam has a more open cell structure. Pore sizes span 150–800 μm for standard polyurethane (PU) foam and 275–1136 μm for polyester polyurethane (PESPU) foam. Air flow rates hit 139 L/min for PU foam and 35 L/min for PESPU foam. The open design creates less flow resistance. Moisture and air pass through with ease.
Physical and Mechanical Properties
Polyester foam gives you greater density and stiffness. It absorbs shock well and fights wear and tear. You get excellent oil resistance, corrosion resistance, and heat tolerance. But polyester soaks up water and can grow mildew in wet conditions. It costs more than polyether.
Polyether foam is more flexible but less durable. Its strength is water resistance and moisture control. Polyether fights moisture damage over long periods. It stops mildew growth better and handles acids and bases well. The special hydrostatic stability makes polyether best for humid or wet spaces. Plus, it costs less.
Application-Specific Customization
Both materials work with special additives during production. Polyester can add anti-static, anti-microbial, flame retardant, or electrostatic properties. Polyether’s compressed, smooth polyurethane structure gives high viscosity rates and strong resistance to wear and cuts.
PPI (Pores Per Inch) Classification and Flow Characteristics
Pore density controls filter performance. PPI counts how many pores cross a one-inch line through the foam. This number shows flow speed, filtration power, and pressure response.
Understanding PPI Measurement
Standard PPI counting uses a 3D computer method for accuracy. Engineers divide the pore space with a marker-based watershed algorithm in the SNOW system. The process begins with binary structure input—gray shows solid material, blue shows pore space. The system removes markers on saddles and plateaus. It filters peak points in signed Euclidean distance function (SEDF). Then it runs watershed division.
The math counts pores along measurement lines in x, y, and z directions. You get PP100C (pores per 100 calibrated units) with this formula: (pores counted × 100) ÷ line length. This number links to Voronoi points. More points create higher PP100C in a fixed space.
PPI and Directional Effects
Stretching the foam shifts PPI in different directions. Apply a 0.5 stretching factor in the z-direction. PP100C_z hits the highest value among all three axes. Smaller stretch in one direction boosts PP100C in the others. Porosity stays constant. PP100C also climbs with porosity if Voronoi points remain fixed.
Flow Performance by PPI Rating
Higher PPI filters (smaller pores) give you faster wicking. You get better filtration power and lower emission. The trade-off? Higher pressure drop across the filter.
Lower PPI filters (larger pores) offer more absorption capacity. Emission goes up. Pressure drop stays minimal. Wicking runs slower than high-PPI types.
Flow rate matches pore size across all pressure ranges. PMI Capillary Flow Porometer data confirms this. Interconnected pores (types 3 and 4) allow bulk flow through the foam. Twisted paths increase travel time. This creates delay compared to straight flow routes.
Flame Retardant (FR) Reticulated Foam Filters
Fire safety rules create demand for special filter materials in high-risk areas. FR reticulated foam filters meet tough safety standards. They also keep great filtration performance. These filters pass UL94 V0 self-extinguishing certification and FMVSS 302 requirements. This makes them vital for automotive, aerospace, and industrial uses where fire risk exists.
Material Structure and Flame Resistance
Makers build FR filters from reticulated polyester or polyether Polyurethane foam. They add fire-blocking chemicals to the foam. The open cell structure keeps 97% void volume for depth loading filtration. This uniform cell design stops open channels that hurt filter efficiency. The foam has density ratings of 1.4-1.9 lb/ft³ (22-30 kg/m³) per ASTM D3574-91 standards. Tensile strength runs from 5-35 psi based on PPI grade. Elongation hits 100-160%. Compression set at 50% deflection shows maximum 15% loss. This proves the foam holds its shape over time.
PPI Grades and Performance Metrics
FR foam filters range from 10 ppi to 60 ppi setups. Common grades include 20, 30, 45, and 60 ppi options. SIF® Felt Grade 900 testing at 500 fpm air velocity shows clear performance profiles:
-
20 ppi oiled: 82% arrestance, 220 gm dust capacity
-
30 ppi oiled: 75% arrestance, 245 gm dust capacity
-
45 ppi oiled: 69% arrestance, 330 gm dust capacity
Pressure drop changes with PPI rating. At 200 fpm, 10 PPI foam shows 0.01 in H₂O resistance. At 800 fpm, resistance climbs to 0.15 in H₂O for 10 ppi. It exceeds 1.0 in H₂O for 100 ppi grades.
Available Specifications
Standard air filter foam keeps 32-36 kg/m³ density with 2.5-4.5 kPa hardness and 250% elongation. Thickness options run from 1/8″ through full bun height in 1/16″ increments. Common sizes include 1/4″, 3/8″, 1/2″, 5/8″, and 3/4″ with ±3mm tolerance. Sheet dimensions come in 2′ × 6′ formats (1 cu.ft.) or metric 2000 × 750mm and 2000 × 1500mm sizes. Compression ratios hit up to 20:1. This gives you tight control over filtration efficiency and particle capture rates.
Fish-Grade and Aquatic Application Filters
Aquarium and aquaculture systems need foam filters without toxic additives. Pentair fish-grade Reticulated foam filters remove fire retardants and germicides. These chemicals harm aquatic life. The filters use 20 ppi density as standard. The open-cell structure catches debris. Plus, it supports helpful bacteria colonies for bio filtration.
Product Specifications and Pricing
Pentair has multiple setups for different tank sizes and filter needs:
-
PF11P5 Fine Grade: 0.30″ thick, 12″ width, 12 yards length, ships at 7 lbs for $48.05
-
PF17A Medium: 1″ thick, 28″ width, 2 yards, 4 lbs, $34.71
-
PF17C Coarse: 2″ thick, 28″ width, 2 yards, $44.58
-
PF16C Coarse: 2″ thick, 28″ width, 4 yards, 7 lbs, $82.02
-
PF8A Fine DSP: 1″ thick, 36″ width, 2 yards, 3 lbs, $19.41
Carbon filter material (PF3) adds chemical filtration. The 0.40″ thick sheets have polyester fibers coated in Activated Carbon. PF4 uses 0.020″ diameter fibers. PF5 uses 0.025″ diameter fibers. This combo handles mechanical, chemical, and biological filtration. You get crystal-clear water.
Flow Rate and Biomedia Requirements
Proper flow rates stop poor water quality. Standard aquarium setups need 4-6 times tank volume per hour in GPH (gallons per hour). A 20-gallon tank requires 80-120 GPH flow. Conservative systems work with 3-4 times tank volume.
Biomedia surface area per pound of fish controls ammonia breakdown and overall health:
|
Surface Area (sq ft/lb) |
Ammonia Level |
Water Clarity |
Fish Health |
300 ppi Foam Life |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
4 |
0-0.5 ppm |
Very dull |
Poor |
1 week |
|
20 |
Undetectable |
Dull |
Decent |
2 months |
|
100 |
Undetectable |
Crystal-clear |
Good |
2 years |
|
500 |
Undetectable |
Crystal-clear |
Excellent |
Never clogs |
Minimum surface area for ammonia control reaches 5 ft²/lb of fish in tilapia or catfish systems with static submerged media. Fish produce 0.775g ammonia per pound each day. FAO standards recommend 0.2-2g/m²/day processing capacity. This equals 2.8-28 ft²/lb for submerged media.
Blackwater species (neon tetras, discus, Oscars) need 40-200 ft²/lb. They’re more sensitive than other fish. Low pH cuts bacterial efficiency. You need 3x surface area at pH 6.5 and 10x at pH 6.0 compared to neutral pH systems.
A 10x10x12″ canister filled with pot scrubbers (620 in³ = 1 ft² surface) gives enough biomedia for 1.9 lb of fish at the 100 ft²/lb standard. Ten fish weighing 82 grams (5″ length) create 1.8 lb metabolic load. This matches the canister capacity exactly.
Felted and Compressed Reticulated Foam Variants
Compression turns standard reticulated foam into dense, high-performance filters. SIF® Felt leads this category. Makers use controlled time, pressure, and heat on reticulated polyester foam. The result? Compressed sheets with exact thickness specs and much more internal surface area.
The Felting Process and Density Boost
Thermal-compressing creates felted foam. It combines mechanical pressure with heat treatment. This process compresses the foam structure for good. Density goes up. Internal surface area grows. These changes improve wicking ability, filtration efficiency, and controlled fluid flow.
Polyester foam compresses well, so it works best for felting. You can make sheets at any thickness you need. The compression step also lets makers add functional extras. Options include anti-static compounds, anti-microbial agents, flame retardants, and electrostatic dissipative treatments.
Reticulation Methods Before Compression
All felted foam starts with closed-cell polyurethane foam. Cell walls need to break open before compression. Three main methods create the open structure:
Alkali hydrolysis submerges soft polyester polyurethane foam in 10% sodium hydroxide solution at 50°C for 10 minutes. Then comes water washing, acetic acid neutralization, a second water wash, and drying. This chemical method opens cells well.
Combustion reticulation uses controlled explosion. Evacuate a container to 13.3 Pa pressure. Add oxygen and natural gas in a 2:1 ratio by volume. Ignition burns away cell membranes. Structural struts stay intact.
Thermal reticulation works in a vacuum chamber with a hydrogen-oxygen mixture. High-speed flame ignition melts cell membranes in polyether or polyester foams in seconds.
Application-Specific Selection Guide
Match your reticulated Foam filter to your exact operational needs. Different industries face unique challenges. Temperature extremes, chemical exposure, particle size targets, and flow rate requirements—all these factors drive your choice.
Industrial Metalcasting and Foundry Operations
molten metal filtration needs ceramic-coated reticulated foam filters rated for 1200°C+ temperatures. Aluminum casting uses 10-20 PPI grades to trap oxide inclusions and dross particles from 50-500 microns. Steel foundries use 20-30 PPI Ceramic foam filters to capture slag and non-metallic impurities before they reach the mold cavity.
Critical selection factors:- Operating temperature range (aluminum: 660-760°C, steel: 1400-1600°C)- Metal flow rate—higher PPI reduces turbulence but increases pressure drop- Impurity load—heavier contamination requires lower PPI for longer filter life- Mold design—filter must fit firmly in gating system without bypass
A 500kg aluminum casting operation uses 8-12 ceramic foam filters per day at $15-35 per unit. Price depends on size and PPI rating.
Aquarium and Aquaculture Systems
Fish-grade foam removes toxic additives found in standard industrial filters. Freshwater tropical tanks need 20-30 PPI polyether foam for mechanical filtration plus biological colonization. The 97% void volume supports beneficial bacteria populations reaching 10^9 CFU per cubic inch in mature biofilms.
System-specific requirements:
– Community tanks (50+ gallons): 30 PPI foam processes 200-300 GPH with minimal clogging
– Breeding systems: 45-60 PPI captures fry-sized particles without excess flow restriction
– Saltwater reef tanks: Polyether foam resists salt breakdown; replace every 18-24 months
– Commercial aquaculture: 10-20 PPI handles high solid loads; clean each week to maintain flow rates
Install 500 ft² biomedia surface per pound of fish in high-density systems. A 100-gallon tilapia tank stocking 30 lbs requires foam media providing 15,000 ft² total surface. You can achieve this with about 24 cubic feet of 300 PPI reticulated foam.
Automotive and Transportation Air Filtration
Flame-retardant polyester foam meeting FMVSS 302 standards protects passenger compartments. Engine intake pre-filters use 20 PPI oiled foam. This achieves 82% arrestance at 500 FPM velocity with 220-gram dust capacity before replacement.
HVAC cabin filters combine 30 PPI FR foam (75% arrestance, 245g capacity) with activated carbon sheets for odor control. Pressure drop stays below 0.25 inches H₂O at normal airflow rates (200-400 CFM). This preserves blower motor efficiency.
Heavy equipment in dusty environments installs 10-15 PPI foam pre-cleaners upstream from paper filters. This two-stage approach extends primary filter life by 300-400%. Construction and mining applications see this benefit where airborne particle concentrations exceed 50 mg/m³.
Key Performance Properties and Testing Standards
Reticulated foam filters go through strict testing to check their strength, chemical resistance, and filtration performance. Labs run these tests before the filters reach industrial use. Standard test methods give you solid data. You can compare different foam types and predict how they’ll perform in real conditions.
Physical and Mechanical Property Testing
Density measurement follows ASTM D3574-91 Test A. Labs cut foam samples to exact sizes and weigh them. Results show up as pounds per cubic foot (lb/ft³) or kilograms per cubic meter (kg/m³). Standard reticulated polyester foam ranges from 1.4 to 1.9 lb/ft³ (22-30 kg/m³). Higher density means more material in the skeletal structure. This boosts durability but can slow down flow rates.
Tensile strength testing per ASTM D3574-91 Test E stretches foam samples until they break. Reticulated foam shows tensile values from 5 psi (low PPI grades) to 35 psi (high PPI grades). The test shows how much pulling force the foam can take before the strut network breaks. Vibration or mechanical stress? You need higher tensile ratings.
Compression set testing checks permanent shape change after sustained pressure. ASTM D3574-91 Test D compresses foam to 50% of original thickness for 22 hours at 70°C. Quality reticulated foam shows maximum 15% permanent compression loss. This matters for filters in sealed housings or stacked filter banks. Good shape retention stops bypass flow.
Elongation testing stretches foam samples and tracks maximum extension before breaking. Most reticulated foam reaches 100-160% elongation. Higher values mean better flexibility. The foam resists tearing during installation or cleaning.
Filtration Performance Metrics
Arrestance efficiency measures particle capture rates at controlled air speeds. SIF® Felt Grade 900 testing at 500 feet per minute (fpm) shows clear performance gaps:
-
20 PPI oiled foam: 82% arrestance with 220-gram dust capacity
-
30 PPI oiled foam: 75% arrestance with 245-gram dust capacity
-
45 PPI oiled foam: 69% arrestance with 330-gram dust capacity
See the pattern? Lower arrestance in higher PPI grades comes with more dust holding capacity. Finer foams have larger total pore volume. They store more particles before clogging.
Pressure drop measurement tracks resistance to airflow across the filter. Testing covers multiple speeds to map full performance curves. At 200 fpm air velocity, 10 PPI foam shows just 0.01 inches H₂O resistance. Boost velocity to 800 fpm and resistance jumps to 0.15 inches H₂O for 10 PPI. It tops 1.0 inches H₂O for 100 PPI grades. These numbers guide HVAC system design and blower motor picks.
Dust holding capacity tests load foam samples with standard test dust (ASHRAE 52.2 synthetic dust). Testing runs until pressure drop doubles from the starting point. Results show in grams of captured particles. Lower PPI foams (10-20 PPI) hold 150-250 grams before you need to replace them. Higher PPI grades (45-60 PPI) stretch capacity to 300-400 grams. Greater internal surface area and depth loading make this possible.
Chemical Resistance and Environmental Testing
Chemical compatibility testing exposes foam samples to specific fluids for long periods. Standard checks test resistance to:
-
Mild acids and alkalis (pH 3-11 range)
-
Petroleum products (fuel, oil, lubricants)
-
Cleaning agents (detergents, solvents)
-
Saltwater and marine environments
Polyether foam keeps its structure in continuous water immersion for 2+ years without breaking down. Polyester foam fights off hydrocarbon exposure. But it absorbs water. This can cause mildew in humid spots without proper treatment.
Temperature range testing checks operational limits. Standard polyurethane reticulated foam works from -30°C to +110°C (-22°F to 230°F). Ceramic-coated types for metalcasting handle 1200-1600°C (2192-2912°F) for short contact with molten metal.
UV aging resistance uses fast weathering chambers with controlled UV exposure cycles. Quality reticulated foam shows little strength loss after 1000 hours equivalent outdoor exposure. This counts for filters in outdoor gear or near windows.
Fire Safety Certifications
UL94 V0 testing checks self-extinguishing properties. Technicians hit vertical foam samples with a Bunsen burner flame for 10 seconds. They remove it, then hit it again for another 10 seconds. V0 rating needs:
-
Flame goes out within 10 seconds after each hit
-
No flaming drips that light cotton below
-
Total flame time under 50 seconds for 5 samples
Flame-retardant reticulated foam earns this certification through chemical additives in the polymer mix.
FMVSS 302 horizontal burn testing tracks flame spread rate in car materials. The test lays foam flat and lights flame to one end. Passing materials show burn rates below 4 inches per minute. All car cabin filters and seat padding must meet this federal motor vehicle safety standard.
Flow Characterization Methods
PMI Capillary Flow Porometry measures pore size spread and connections through controlled pressure/flow testing. The system:
-
Soaks foam with low surface tension wetting liquid
-
Builds gas pressure to push liquid from pores
-
Records pressure and flow rate at each step
-
Figures out pore sizes from bubble point math
Results show pore type spread (isolated vs. connected), mean flow pore size, and twist factors. These predict filtration performance better than PPI count alone.
Wicking speed testing times how fast liquid moves through foam via capillary action. Higher PPI foam wicks faster (more capillary paths). Lower PPI grades wick slower but soak up more total volume. This controls fluid spread in inkjet printer heads, medical wound dressings, and battery separators.
Industry-Specific Test Standards
Aquarium biomedia surface area measurement uses methylene blue dye absorption testing. Known dye amounts flow through foam samples. Spectrophotometer checks measure dye removal. Results figure total internal surface area for bacterial colonies. Critical for biological filtration power.
metal casting filter performance testing checks Ceramic foam filters through:
-
Crushing strength (fights metallostatic pressure)
-
Thermal shock resistance (fast heating/cooling cycles)
-
Slag/inclusion capture efficiency (microscope checks of filtered metal samples)
Quality ceramic foam filters show >90% removal of particles >50 microns in aluminum casting jobs.
These standard testing steps give you hard data for comparing filter choices. They help predict service life, maintenance timing, and total cost across different working conditions.
Conclusion
Finding the right reticulated foam filter means matching three things: material chemistry, pore structure, and treatments. These need to fit your exact needs. You might filter molten metal with polyester foam. Or manage airflow in HVAC systems with specific PPI ratings. Or ensure aquatic safety with fish-grade types. Each one serves a clear purpose.
Ready to pick the perfect reticulated foam filter for your project? Start with three key factors: operating temperature, filtration micron level, and exposure conditions. These will narrow your options fast. You’ll invest in a filter that performs, not just one that fits.